Figure 1.
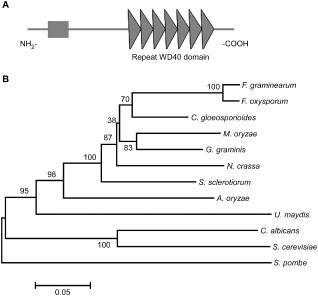
Functional domain identification and phylogenetic tree. A. Prediction of domains in MoTup1 using the SMART website. B. Sequence alignments were performed using the Clustal_W program and the calculated phylogenetic tree was viewed using Mega4.1 Beta program. Neighbor‐joining tree with 500 bootstrap replicates of phylogenetic relationships between Tup1 homologues in fungi. All of the Tup1 proteins were downloaded from the NCBI database and their accession numbers are as following: M. oryzae (Magnaporthe oryzae XP_003717030.1), F. graminearum (Fusarium graminearum XP_382677.1), F. oxysporum (Fusarium oxysporum EGU83576.1), C. gloeosporioides (Colletotrichum gloeosporioides XP_007281086.1), G. graminis (Gaeumannomyces graminis EJT80144.1), N. crassa (Neurospora crassa XP_956212.1), S. sclerotiorum (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum XP_001596040.1), A. oryzae (Aspergillus oryzae XP_001727812.1), U. maydis (Ustilago maydis XP_759427.1), C. albicans (Candida albicans XP_713297.1), S. cerevisiae (Saccharomyces cerevisiae AAA35182.1) and S. pombe (Schizosaccharomyces pombe AAB81475.2).
