Figure 5.
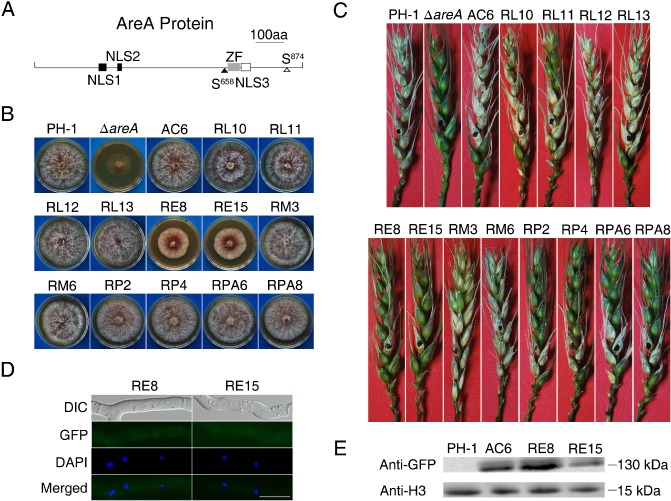
Site‐directed mutagenesis analysis with the AREA gene. (A) The AreA protein is predicted to have three conserved nuclear localization signal (NLS) sequences (NLS1, 238–244; NLS2, 287–290; NLS3, 716–725), one consensus protein kinase A (PKA) (S874) and one mitogen‐activated protein kinase (MAPK) (S658) phosphorylation site, and one zinc figure domain (ZF, 686–710). (B) Four‐day‐old potato dextrose agar (PDA) cultures of the wild‐type strain PH‐1, ΔareA mutant, ΔareA/ AREAΔNLS1‐GFP (RL10 and RL11), ΔareA/ AREAΔNLS2‐GFP (RL12 and RL13), ΔareA/ AREAΔNLS3‐GFP (RE8 and RE15), ΔareA/ AREAΔS874‐GFP (RP2 and RP4), ΔareA/ AREAΔS657 ‐658‐GFP (RM3 and RM6) and ΔareA/ AREAS874A‐GFP (RPA6 and RPA8) transformants, and complementation strain (AC6). (C) Wheat heads inoculated with the same set of strains were examined for scab symptoms at 14 days post‐inoculation (dpi). (D) Germlings of transformants RE8 and RE15 were stained with 4′,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole (DAPI) and examined by differential interference contrast (DIC) or epifluorescence microscopy. GFP, green fluorescent protein. Bar, 10 μm. (E) Western blot analysis with total proteins isolated from vegetative hyphae of PH‐1 and ΔareA/ AREAΔNLS3‐GFP transformants RE8 and RE15. The AreA‐GFP band was detected with the anti‐GFP antibody. Detection with an anti‐H3 antibody was used as the control to show that similar amount of proteins were loaded in each lane.
