Figure 6.
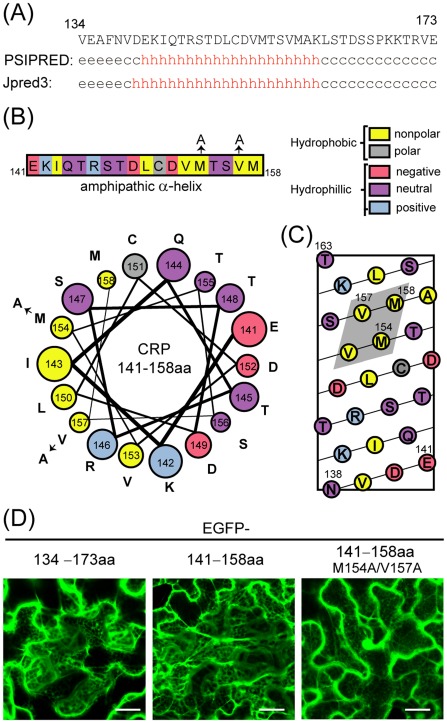
Role of the C‐terminal amphipathic α‐helical region in the association of Chinese wheat mosaic virus (CWMV) cysteine‐rich protein (CRP) with endoplasmic reticulum (ER). (A) Secondary structure predictions of the C‐terminal 40 amino acids of CWMV CRP using psipred and Jpred3. The predicted structures are indicated as helical (h), strand (e) or undetermined (c, coil). (B) Linear and helical wheel projections of CWMV CRP amino acids 141–158. Colour coding indicates amino acid characteristics. Amino acids that were substituted by alanine are indicated by arrows. (C) A helical net projection of CWMV CRP amino acids 138–163. The potential hydrophobic patch is shaded. (D) Subcellular localization of enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) fused to the C‐terminal 40 amino acids (134–173aa), the predicted α‐helical region (141–158aa) or its substitution mutant (141–158aa M154A/V157A) of CWMV CRP. GFP fluorescence was observed using confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) at 3 days after inoculation (dai). Bars, 25 μm.
