Figure 6.
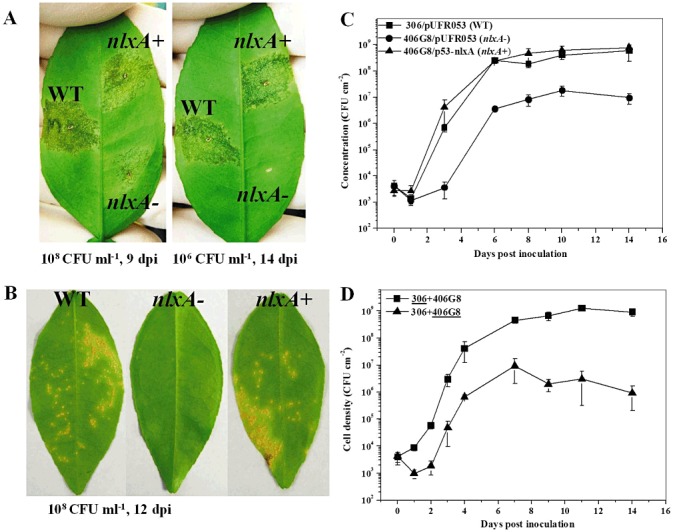
The nlxA gene is important for the virulence and growth in planta of Xanthomonas citri ssp. citri. Grapefruit (Citrus paradise Macf. cv. Duncan) was used for virulence and growth assay. For virulence assay, the wild‐type, nlxA mutant and complementary strain were inoculated into the intercellular spaces (A) or sprayed onto the leaf surfaces (B) of grapefruit. The inoculation concentration of the cell suspensions and the incubation time for photography are shown. The experiments were repeated more than three times with similar results. Only one representative leaf was photographed and presented. For in planta growth assay (C), the wild‐type, nlxA mutant and complementary strain were inoculated into the intercellular spaces of the leaves with a cell suspension of 5 × 105 colony‐forming units (CFU)/mL. For co‐inoculation growth assay (D), cell suspensions (106 CFU/mL) of the wild‐type and nlxA mutant were mixed equally and inoculated into the leaves following the same method. The growth curves of the wild‐type and the nlxA mutant in the co‐inoculation experiment are indicated by underlining. Bacterial cells from the inoculated leaves were recovered at different time points. The in planta growth was measured in quadruplicate and the assays were repeated three times independently. Means and standard errors of four replicates from one representative result are shown. Vertical bars represent the standard errors of the means.
