Figure 1.
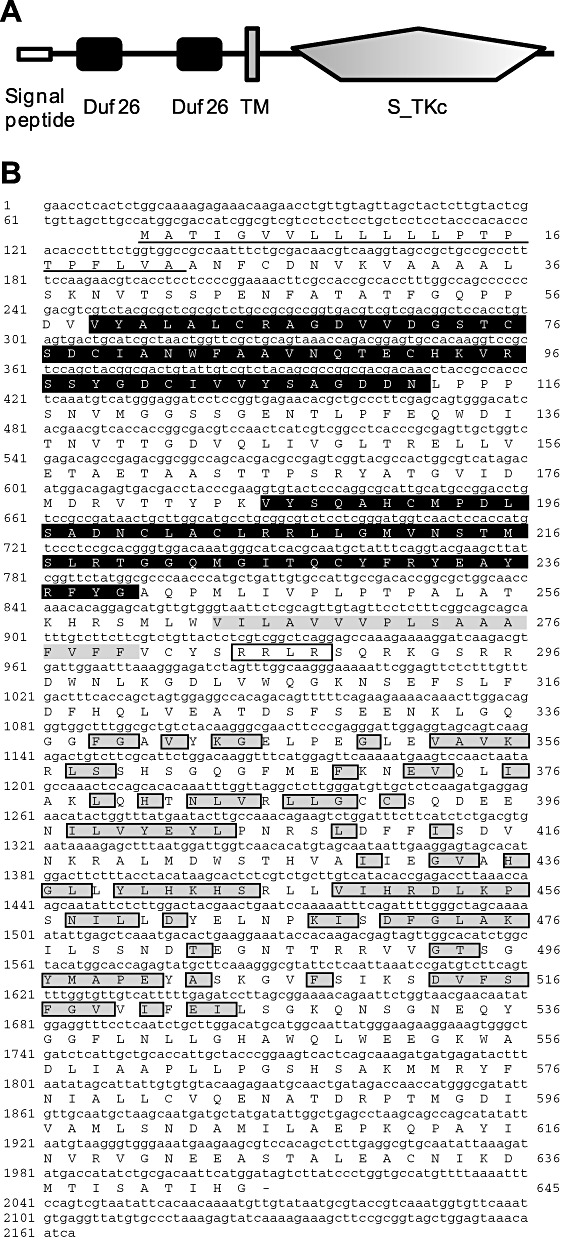
Domain architecture, deduced amino acid sequence and phylogenetic analysis of Hordeum vulgare cysteine‐rich receptor‐like protein kinase (HvCRK1). (A) Schematic diagram of HvCRK1 protein domain architecture showing the signal peptide and two characteristic domain 26 of unknown function (duf26) domains at the N‐terminus, followed by a transmembrane TM domain and a well‐conserved kinase domain. (B) Deduced amino acid sequence of HvCRK1, showing two duf26 domains (highlighted in black), TM domain (highlighted in grey) and the kinase domain (following the TMD). Conserved amino acids in the predicted serine–threonine kinase domain are highlighted in grey boxes (National Center for Biotechnology Information conserved domain search; http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov).
