Figure 3.
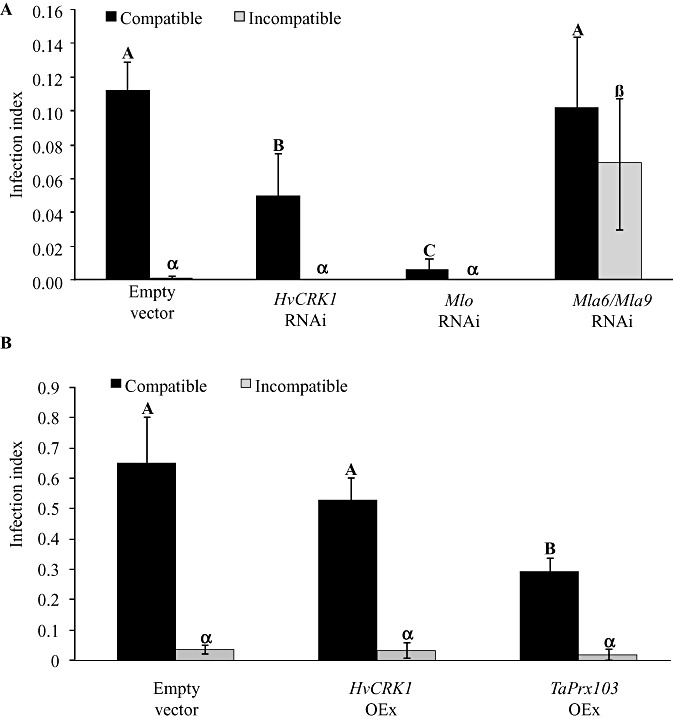
Effects of silencing (RNAi) or overexpression (OEx) of Hordeum vulgare cysteine‐rich receptor‐like protein kinase (HvCRK1) on barley responses to Blumeria graminis f.sp. hordei (Bgh) attack. Bgh infection is given as the infection index, which is the number of haustoria divided by the total number of transformed cells. (A) Bgh infection of barley cells transiently expressing empty vector as control (pIPKTA30N), the RNAi construct for HvCRK1 (pIPKTA30_CRK1), the RNAi construct for Mlo (pIPKTA36) or the RNAi construct for Mla6 and Mla9 (pIPKTA30_Mla6). In the compatible interaction, silencing of HvCRK1 resulted in reduced infection, when compared with empty vector or RNAi against Mla6/Mla9, which have no function in the compatible interaction. RNAi against Mlo gave the expected strong reduction in Bgh infection. In the incompatible interaction, there was no infection as a result of Mla9 R‐gene‐mediated programmed cell death (PCD) of Bgh‐infected cells, except for RNAi against Mla6/Mla9 which silenced the R gene and allowed Bgh infection. (B) Bgh infection of barley cells transiently overexpressing the empty vector as control (pIPKTA9), overexpression of HvCRK1 (pIPKTA9_CRK1) or overexpression of the peroxidase gene TaPrx103 (pWIR3). In the compatible interaction, overexpression of HvCRK1 had no effect on Bgh infection. Overexpression of TaPrx103 gave the expected reduction in Bgh infection. In the incompatible interaction, there was no infection as a result of Mla9 R‐gene‐mediated PCD of Bgh‐infected cells. The infection index is given as the mean ± standard error, and different letters or symbols within each interaction indicate significant differences (n= 5, P= 0.05).
