Figure 5.
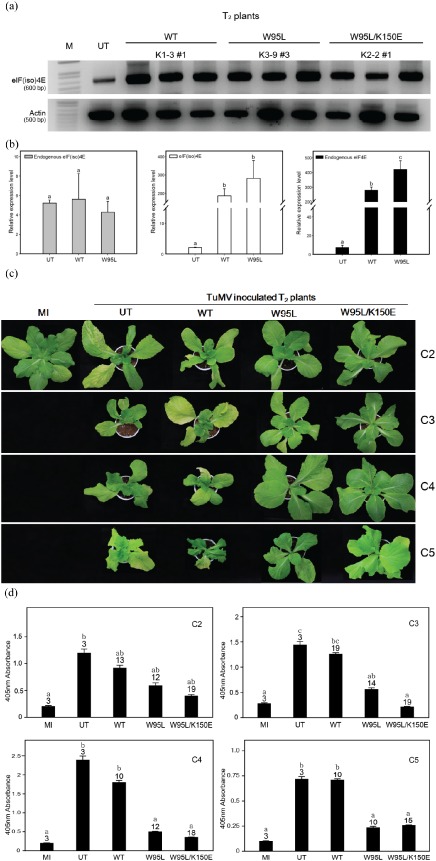
Turnip mosaic virus (TuMV) screening of T 2 transgenic Chinese cabbage over‐expressing eIF(iso)4E [eukaryotic initiation factor(iso)4E] mutants. (a) Reverse transcription‐polymerase chain reaction (RT‐PCR) analysis to test the expression of the eIF(iso)4E transgenes. M, DNA marker; UT, untransformed control; WT, Samjin eIF(iso)4E wild‐type transformant; W95L, eIF(iso)4E W95L mutant transformant; W95L/K150E, eIF(iso)4E W95L/K150E transformant. (b) Profiles of gene expression level of endogenous eIF(iso)4E, introduced eIF(iso)4E and endogenous eIF4E by quantitative real‐time RT‐PCR. The relative expression level of each gene, which was normalized using the actin reaction product, was defined by an arbitrary unit. Values represent mean ± standard errors. Different letters denote statistically significantly different values [analysis of variance (ANOVA), P ≥ 0.05]. UT, untransformed control; WT, Samjin eIF(iso)4E wild‐type transformant; W95L, eIF(iso)4E W95L mutant transformant. (c) Phenotypes of TuMV‐inoculated eIF(iso)4E T 2 plants. The plants were photographed at 45 days post‐inoculation (dpi). (d) Enzyme‐linked immunosorbent analysis (ELISA) screening after TuMV CHN2, CHN3, CHN4 and CHN 5 inoculation. Double antibody sandwich (DAS)‐ELISA was performed at 45 dpi to assess virus accumulation using the fifth and sixth true leaves. MI, mock‐inoculated; UT, untransformed ‘Seoul’ cultivar. The numbers on each bar indicate the total number of T 2 plants that were screened. Error bars represent standard deviation. Different letters denote statistically significantly different values (ANOVA, P ≥ 0.05).
