Figure 3.
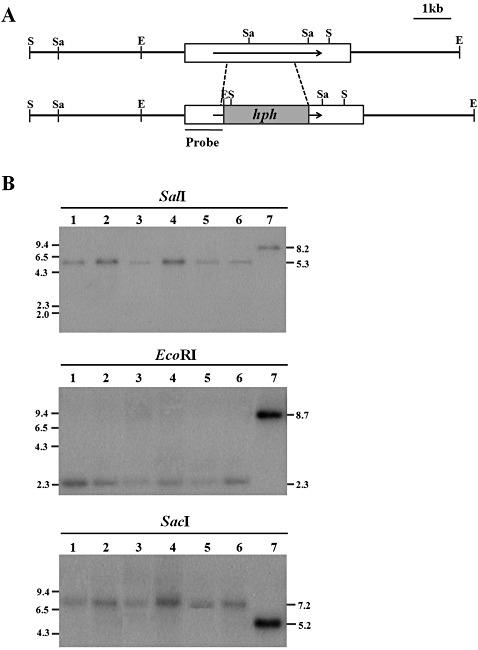
Restriction map and Southern blot analyses of CpSte11 null mutants and wild‐type EP155/2. (A) Restriction map of the CpSte11 genomic region and the expected replaced allele of the CpSte11 gene as a result of double homologous recombination. Boxes indicate the genomic region for the construction of the gene replacement vector pDSTE11, which replaced the internal 1932 bp with the hygromycin B resistance gene (hph), resulting in 1095‐ and 1322‐bp fragments as the 5′ and 3′ flanking regions, respectively. Arrows indicate the direction of transcription. E, EcoRI; S, SalI; Sa, SacI. (B) Southern blot analysis of the wild‐type EP155/2 strain (lane 7) and the CpSte11 null mutants TdSTE11‐3, ‐17, ‐56, ‐74, ‐78 and ‐85 (lanes 1–6). Enzymes used to digest the DNA samples are indicated above the lane numbers and the probe is indicated on the restriction map in (A). Numbers on the right and left indicate the size in kilobases. The CpSte11 null mutants underwent the desired replacement at CpSte11, as indicated by the expected changes in the sizes of the bands that hybridized with the probe.
