Figure 1.
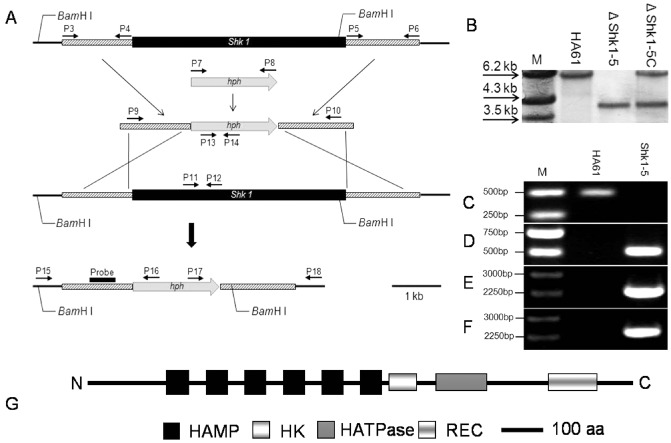
Generation and identification of Shk1 gene deletion mutants and the domain structure of Shk1 in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. (A) Gene replacement strategy for Shk1. The hygromycin resistance cassette (hph) is denoted by the large grey arrow. Primer (P3–P18) binding sites are indicated by arrows (see Table 1 for the primer sequences). (B) Southern blot hybridization analysis of strains using the 5′‐flanking region of Shkl as a probe. Genomic DNA of the wild‐type progenitor HA61, Shk1 deletion mutant ΔShk1‐5 and complemented strain ΔShk1‐5C were digested with Bam HI. (C) Primer pair P11/P12 was used to specifically amplify the partial Shk1 (482 bp). (D) Primer pair P13/P14 was used to validate the selectable marker hph (503 bp). (E, F) Primer pairs P15/P16 and P17/P18 were used to amplify the two homologous arms with a partial fragment of the connecting area (2255 bp in E and 2333 bp in F). (G) Schematic representation of the domain structure of the two‐component histidine kinase gene (Shk1) in S. sclerotiorum. aa, amino acid.
