Figure 6.
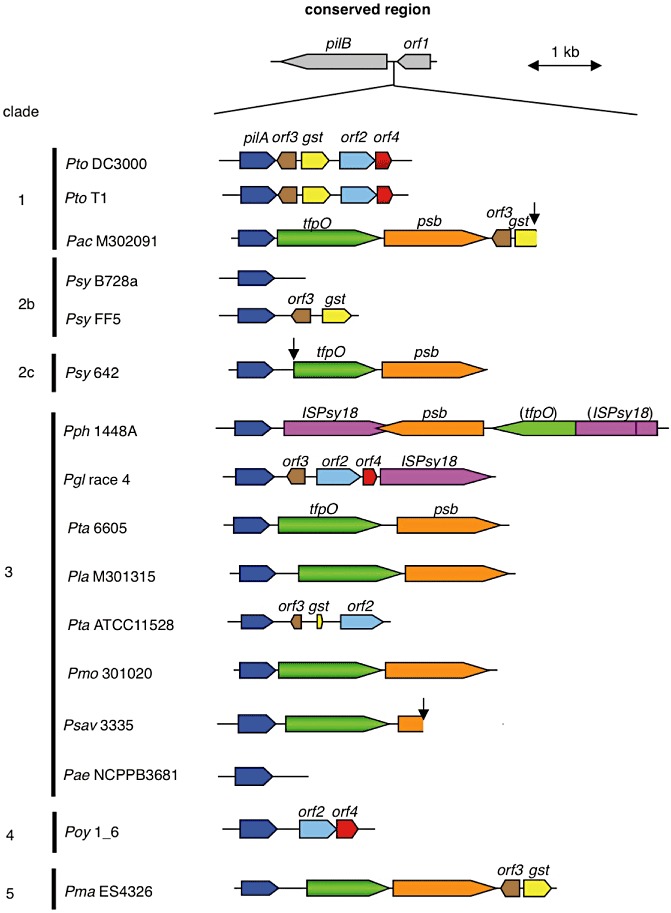
Schematic organization of pilA and its surrounding region in Pseudomonas syringae pathovars. The pilA clusters are flanked by conserved genes encoding for type IV pilus biogenesis protein pilB and orf1. The genes having the same hypothetical function are shown in matching colours: pilA (blue), tfpO (green), psb (orange), gst (for glutathione S‐transferase, yellow), orf2 (light blue), orf3 (brown), orf4 (red) and ISPsy18 (for ISPsy18 transposase, violet). The clusters are compared among P. syringae pathovars/strains whose genome sequences have been analysed so far. The abbreviations of each bacterial name and those of each Entrez Genome Project number (or RefSeq accession number where there is no Genome Project entry) are as follows: P. syringae pv. tomato DC3000 (Pto DC3000, AE016853), pv. tomato T1 (Pto T1, RefSeq accession NZ_ABSM00000000), pv. actinidiae M302091 (Pac M302091, AEAL00000000), pv. syringae B728a (Psy B728a, CP000075), pv. syringae FF5 (Psy FF5, ACXZ00000000), pv. syringae 642 (Psy 642, ADGB00000000), pv. phaseolicola 1448A (Pph 1448A, CP000058), pv. glycinea race 4 (Pgl race4, AB683862), pv. tabaci 6605 (Pta 6605, AB571112), pv. lachrymans M301315 (Pla M301315, AEAF00000000), pv. tabaci ATCC 11528 (Pta ATCC11528, ACHU00000000), pv. mori 301020 (Pmo 301020, AEAG00000000), P. savastanoi pv. savastanoi NCPPB 3335 (Psav 3335, ADMI00000000), pv. aesculi NCPPB3681 (Pae NCPPB3681, RefSeq accession NZ_ACXS01000159), pv. oryzae 1_6 (Poy 1_6, ABZR00000000) and pv. maculicola ES4326 (Pma ES4326, AEAK00000000). The clades of P. syringae species were classified by the high‐throughput genome sequencing approach as reported by Studholme (2011). The arrows indicate the truncated sequence contigs.
