Figure 1.
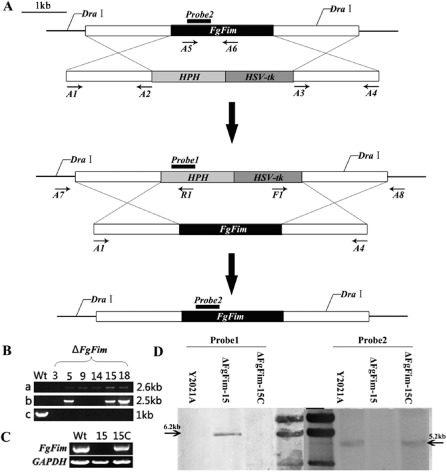
Generation and identification of Fusarium graminearum FgFim gene deletion mutants. (A) Gene replacement and complementation strategy for the FgFim gene. The gene replacement cassette HPH‐HSV‐tk contains the hygromycin resistance gene and the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Primer binding sites are indicated by arrows (see Table S1 for the primer sequences). (B) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) strategy to screen ΔFgFim transformants: a, PCR performed with primer pair A7/R1; a 2.6‐kb amplified fragment indicates ΔFgFim integration at the left junction; b, PCR performed with primer pair F1/A8; a 2.5‐kb amplified fragment indicates ΔFgFim integration at the right junction; c, PCR performed with primer pair A5/A6; a 1.0‐kb amplified fragment indicates a parental gene locus. (C) Reverse transcription‐polymerase chain reaction (RT‐PCR) analysis for the expression of the FgFim gene in the parental isolate (Y2021A), the gene disruption mutant ΔFgFim ‐15 and the complemented transformant ΔFgFim ‐15 C using cDNA as template. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde‐3‐phosphate dehydrogenase. (D) Southern blot hybridization analysis of Y2021A, ΔFgFim ‐15 and ΔFgFim ‐15C using a 485‐bp hygromycin‐resistant gene (hph) fragment as probe1, a 460‐bp FgFim fragment as probe2, and genomic DNA digested with DraI.
