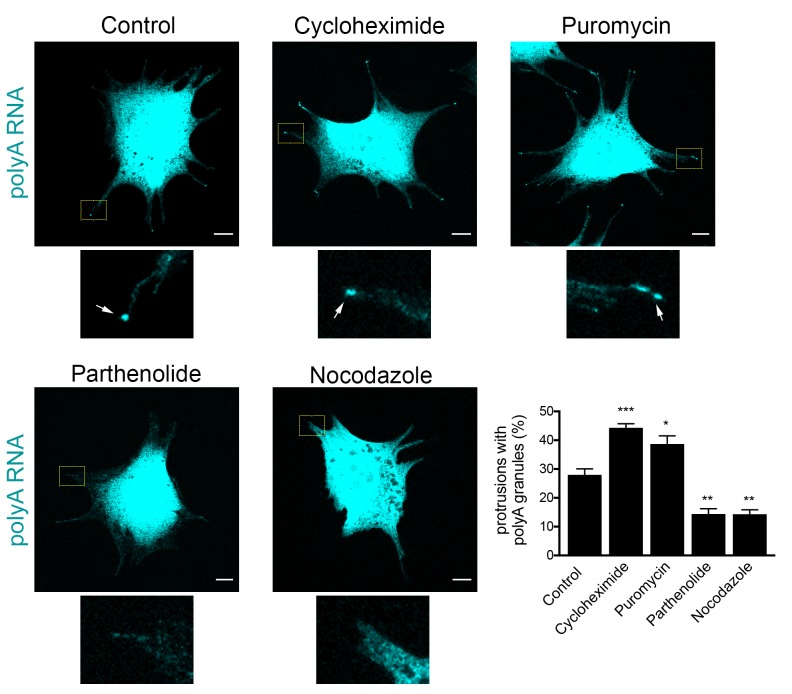
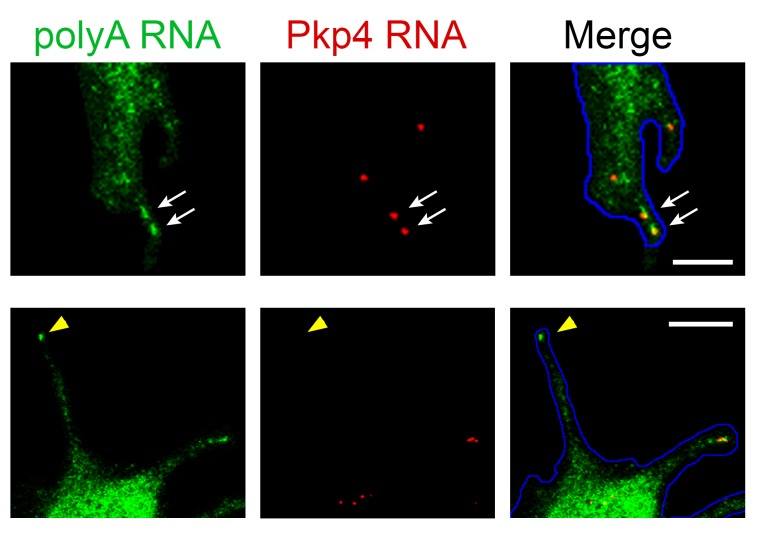
Figure 10. Formation of RNA clusters at protrusions is promoted by translational inhibition and requires microtubules.
PolyA RNA was detected in NIH/3T3 cells with the indicated treatments. Boxed regions are enlarged to show the presence (arrows) or absence of polyA RNA granules at the tips of protrusions. Graph shows scoring of protrusions for the presence of polyA RNA granules. Values are mean and standard error of at least three independent experiments. For each experiment approximately 300 protrusions from more than 25 cells were observed. p-value: *<0.02, **<0.01, ***<0.001 by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test, compared to control. Scale bars: 10 μm.