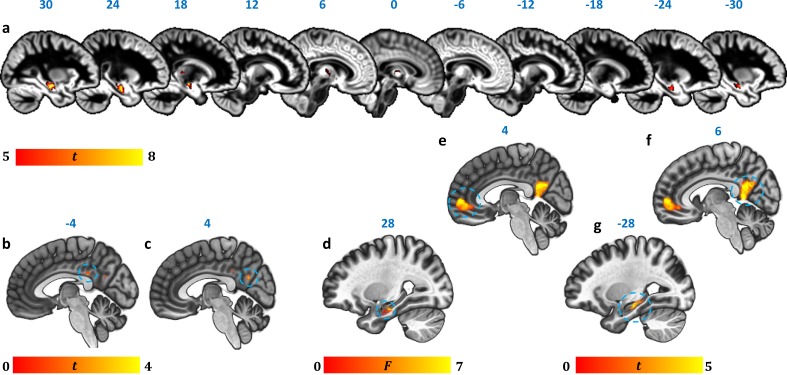
Figure 2. Reduction in GM volume, rsALFF and rsFC in autoimmune LE patients.
(a) A whole-brain VBM on GM volume (contrast: controls > patients) showed volume reduction in patients’ HPC bilaterally, as well as in mediodorsal-anterior and right dorsolateral thalamic regions (Table 4); clusters survive FWE peak-level correction (p<0.05) over p<0.001 unc; color bar indicates t values; b-c: Reduced rsALFF in patients in (b) the posterior cingulate (kE = 89, p-FWE = 0.033; peak voxel coordinates: −4,–36, 28) and (c) precuneus (kE = 137; p-FWE = 0.003; peak voxel coordinates: 4,–60, 26); d-j: reduced rsFC in patients; d: a whole-brain MVPA (omnibus F) showed abnormal rsFC for patients in a cluster in the right HPC (kE = 178, p-FWE = 0.001; peak voxel coordinates: 28,–16,−20; color bar indicates F values); e-g: reduced rsFC of the right HPC (whole-brain seed-to-voxel analysis; seed: right HPC, anatomically delineated in native space, unsmoothed timeseries; contrast: controls > patients); e: medial prefrontal cortex (kE = 1152, p-FWE <0.0001, peak voxel coordinates: 4, 56, 2); f: posteromedial cortex (posterior cingulate, retrosplenial cortex, precuneus; kE = 986, p-FWE <0.0001, peak voxel coordinates: 6,–50, 8); g: left HPC (kE = 393, p-FWE <0.0001, peak voxel coordinates: −12,–36, 2). All rsFC and rsALFF clusters survive FWE correction (p<0.05) for cluster size over an individual voxel threshold of p<0.001; FWE: family-wise error; HPC: hippocampus; kE: cluster size (number of voxels); rsALFF: Resting-state amplitude of low frequency fluctuations; rsFC: Resting-state functional connectivity; VBM: voxel-based morphometry.