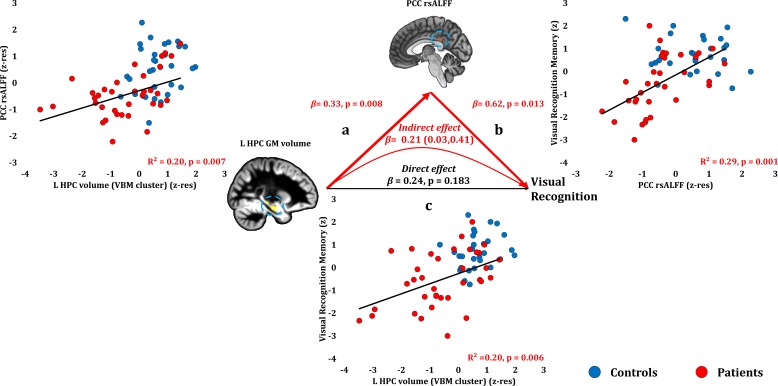
Figure 4. Visual Recognition Memory: Structural/Functional correlates.
(a) mean GM volume of the left HPC cluster correlated with the mean rsALFF of the PCC cluster across patients; (b) visual recognition memory scores correlated across patients with their mean rsALFF in the PCC cluster, surviving correction for multiple testing for the 13 structural/functional abnormalities examined (r = 0.54, p-corr = 0.014); the mediation analysis demonstrates that this effect held over and above the correlation of PCC rsALFF with the mean GM volume of the left HPC cluster; (c) mean GM volume of the left HPC cluster correlated with visual recognition memory scores across patients, but did not survive correction for multiple testing (r = 0.45, p-corr = 0.072); however, the mediation analysis demonstrated that this relationship did not hold over and above the correlation of the mean GM volume of the left HPC cluster with the mean PCC rsALFF; there was only an indirect effect of reduced HPC GM volume on visual recognition memory (within parenthesis: 95% confidence intervals); GM: gray matter; HPC: hippocampus; L: left (hemisphere); MAP: Memory and Amnesia Project; OPTIMA: Oxford Project To Investigate Memory and Aging; p: significance values are presented at uncorrected levels; PCC: posterior cingulate cortex; rsALFF: resting-state amplitude of low frequency fluctuations; TIV: total intracranial volume; VBM: voxel-based morphometry; z: memory scores are averaged age-scaled and standardized scores of participants’ performance in the subtests of interest; z-res: GM volumes from VBM clusters are residualized against age, sex, scan source (MAP, OPTIMA), and TIV across participants; mean rsALFF values are residualized across participants against age and sex.