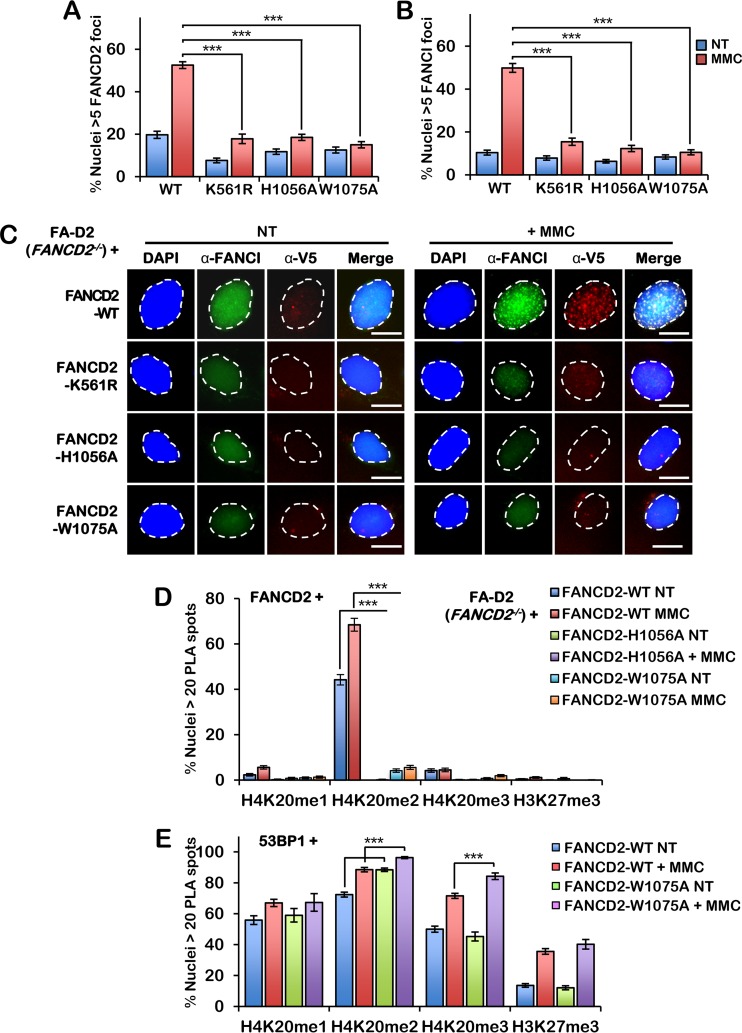
FIG 4.
FANCD2 HBD/MBD mutants fail to assemble into nuclear foci or interact with H4K20me2. (A and B) FA-D2 cells stably expressing wild-type FANCD2, FANCD2-K561R, FANCD2-H1056A, and FANCD2-W1075A were incubated in the absence or presence of 200 nM mitomycin C (MMC) for 24 h. Cells were fixed and stained with anti-FANCI (green) and anti-V5 (red) antibodies and counterstained with DAPI (blue). (A) Quantification of FANCD2 nuclear foci. (B) Quantification of FANCI nuclear foci. Nuclei with >5 V5 (FANCD2) or FANCI foci were considered positive. (C) Representative images from the assay whose results are presented in panels A and B. Bars, 10 μm. (D) Quantification of proximity ligation assay (PLA) results with FANCD2 and H4K20me1, H4K20me2, H4K20me3, and H3K27me3 in FA-D2 cells stably expressing wild-type FANCD2, FANCD2-H1056A, and FANCD2-W1075A. (E) Quantification of PLA results with 53BP1 and H4K20me1, H4K20me2, H4K20me3, and H3K27me3 in FA-D2 cells stably expressing wild-type FANCD2 or FANCD2-W1075A. Nuclei with >20 PLA spots were considered positive. Experiments were performed three times with similar results. At least 300 nuclei were scored per biological replicate. Error bars represent the standard errors of the means from three independent experiments. P < 0.001.