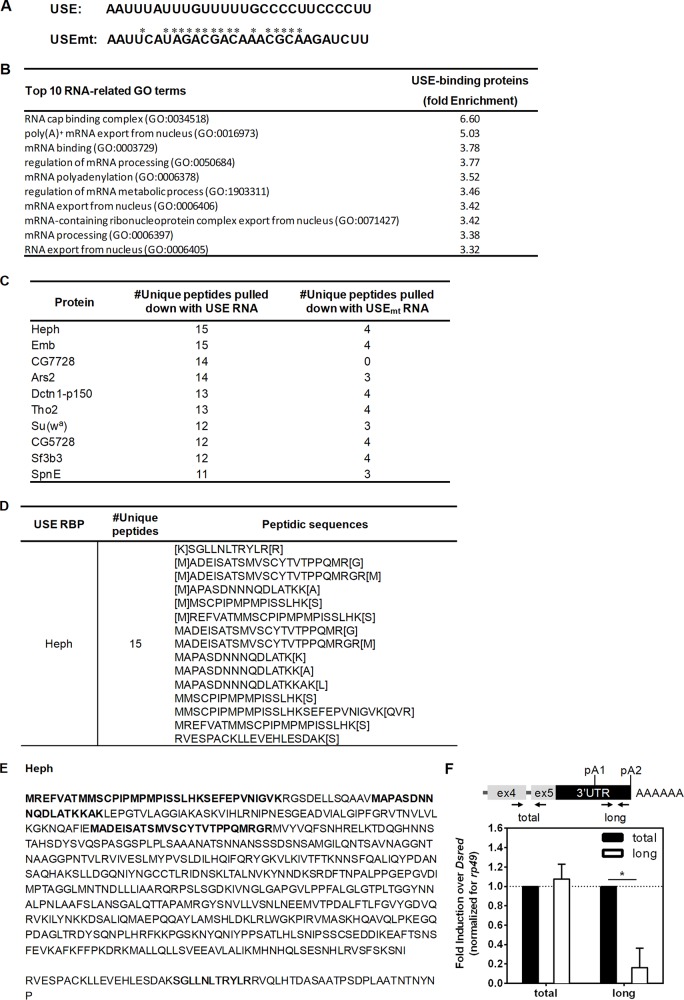
FIG 3.
Heph binds to polo USE RNA. (A) Sequences of the USE and USEmt RNAs used in the RNA-protein pulldown assay (5′ to 3′). *, point mutation in relation to the USE RNA. (B) Top 10 RNA-related GO terms enriched in the proteins that bind to the USE RNA detected by LC-MS/MS. (C) List of the top 10 RNA-related proteins obtained in LC-MS/MS that bind to the USE (number of unique peptides ≥ 5) and do not bind to USEmt (number of unique peptides < 5) ordered from largest to smallest number of unique peptides identified per protein. (D) Numbers of unique peptides and respective sequences identified by LC-MS/MS for Heph (corresponding to the UniProtKB entries Q7KRS7, A0A0B4K6W9, E1JJ45, Q7KES3, and Q8MT11). (E) Amino acid sequences of Heph with the peptidic sequences identified by LC-MS/MS highlighted in bold. From the LC-MS/MS data, the Heph UniProtKB entry Q7KRS7 sequence is depicted, which also includes the sequences of the A0A0B4K6W9, E1JJ45, and Q7KES3 entries. The Heph UniProtKB entry Q8MT11 sequence is truncated and shown below. (F) The longest polo mRNA levels are decreased upon 96 h of heph knockdown. polo mRNA isoform expression levels were measured by RT-qPCR with specific oligonucleotides targeting both polo mRNA isoforms (total) and the longest mRNA isoform (long). rp49 was used as a housekeeping gene. Fold induction over DsRed is displayed (DsRed was set to 1).