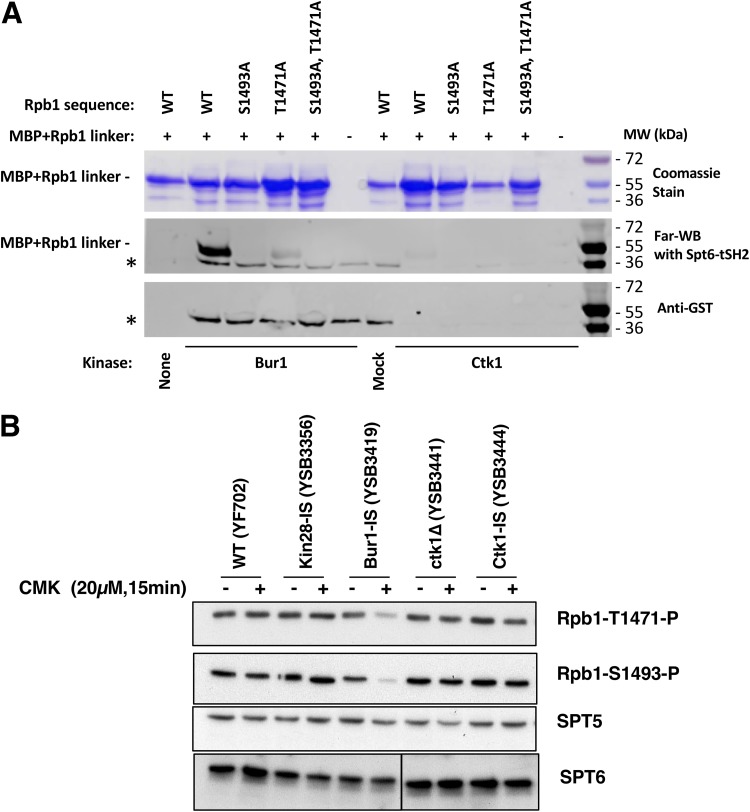
FIG 5.
Bur1 phosphorylates Rpb1 linker region residues that mediate interaction with the Spt6 tSH2 domain. (A) Phosphorylation by Bur1 or Ctk1 enhances in vitro binding of Spt6-tSH2 to an Rpb1 linker peptide. MBP fusions to the Rpb1 linker (residues 1456 to 1511) or mutated derivatives thereof were purified and then incubated with partially purified His12-Bur1, His12-Ctk1, or the corresponding mock purification fractions from an untagged strain. Proteins were split and separated by SDS-PAGE. One aliquot was stained with Coomassie blue (top panel) to show the amounts and purity of the MBP-Rpb1 linker proteins. A second aliquot was transferred to nitrocellulose, refolded, and then probed with GST-Spt6 tSH2, which was subsequently detected using antibodies against GST (middle panel, Far-WB). Strong binding to the WT linker peptide was observed after treatment with Bur1, but this was diminished in mutants lacking the sites previously shown to be important for this interaction (25) (S1493 and T1471). Ctk1 also supported binding at a lower level. The asterisk denotes a species found in the Bur1, mock, and, to a lesser extent, Ctk1 preparations that directly bound the anti-GST antibody, as can be seen in a parallel blot with GST-Spt6 tSH2 protein omitted (bottom panel, anti-GST). (B) The indicated yeast strains were analyzed before or after 15 min of inhibition with 20 μM CMK. Blots were probed with the antibodies specific for Rpb1 linker sites (see Fig. S3B in the supplemental material) or Spt5 and Spt6 as loading controls. Note that the Spt6 bands are all from the same exposure of a single blot, but intervening lanes were removed.