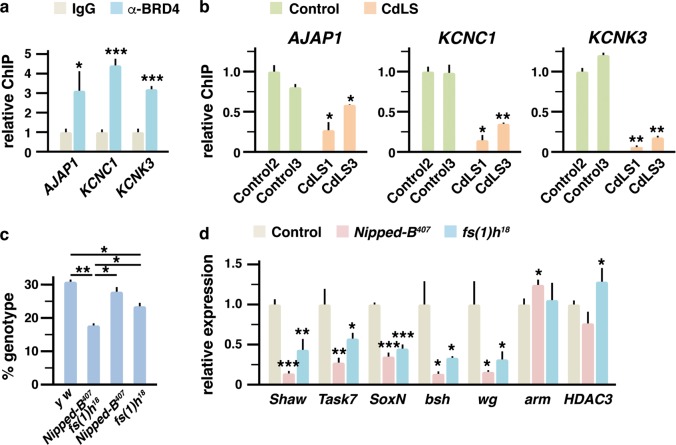
Fig. 6. NIPBL–BRD4 relationship in different cellular models.
a Localization of BRD4 at the promoters of the indicated genes was assessed in human fibroblasts from Control2 healthy donor (see “Materials and methods”) through ChIP analysis with BRD4 antibody (α-BRD4) in comparison with normal rabbit IgG. Relative ChIP levels for each gene were represented. Values are means ± s.d. from three independent experiments analyzed in triplicate. b BRD4 localization at the promoters of the indicated genes was assessed through ChIP analysis in fibroblasts from two healthy donors (Control2 and Control3) or from two CdLS probands with NIPBL mutations (CdLS1 and CdLS3). Relative ChIP levels for each gene were represented. Values are means ± s.d. from two independent experiments analyzed in triplicate. c Quantification of the proportion of the different genotypes in the female progeny from flies crosses between Nipped-B407 males and fs(1)h18 females. Values are means ± s.d. Data correspond to the analysis of 107 individuals from two independent experiments. d Expression levels of the indicated genes as determined in single heterozygous Nipped-B407 and fs(1)h18 flies and in y w controls, were determined by qPCR. Relative levels of expression are represented. Statistical significance of differences between the various conditions and IgG (a), control2 (b), or y w control (d) is indicated on top of each bar. Statistical significance of differences between other conditions is indicated with a line. Significance was analyzed by Student’s t test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001)