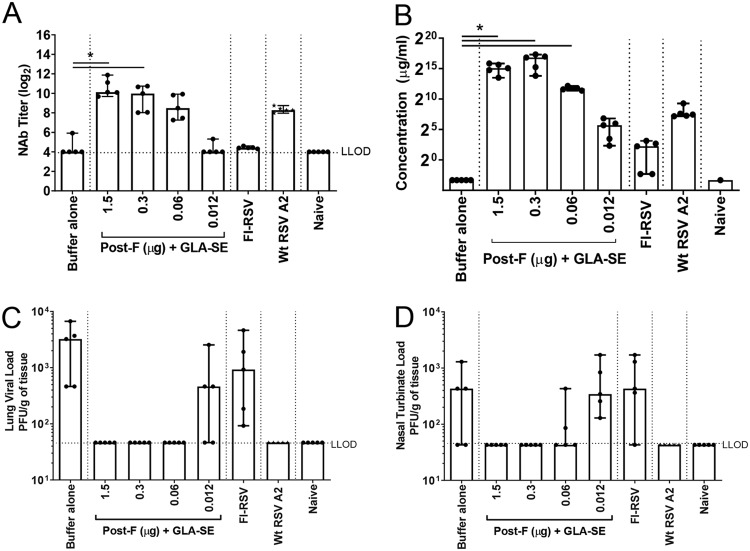
FIG 1.
Immunogenicity induced by decreasing doses of post-F antigen. BALB/c mice (7 weeks old; n, 5 per group) were immunized i.m. at day 0 and day 21 with either buffer alone, different doses of post-F antigen with GLA-SE (2.5 μg GLA in 2% SE) as an adjuvant, or FI-RSV. A control group for natural infection was immunized i.n. with live RSV (106 PFU) at day 0. At day 34, animals were challenged i.n. with 106 PFU of wild-type (wt) RSV A2. Naïve animals were left untreated. (A) Prior to challenge (day 33), sera were harvested, and NAb titers were evaluated using a microneutralization assay. Data are presented as the log2 dilution of serum that provides a 50% reduction in viral entry with an LLOD of 4 (indicated by a dashed line). (B) At sacrifice (day 39), RSV F-specific total IgG was measured by ELISA. For panels A and B, Kruskal-Wallis analyses comparing the experimental groups with the buffer-alone group were performed, followed by pairwise Dunn’s multiple-comparison tests. *, P < 0.05. (C and D) Lung (C) and nasal turbinate (D) viral loads were determined by plaque assays. Medians, with ranges of individual values, are shown.