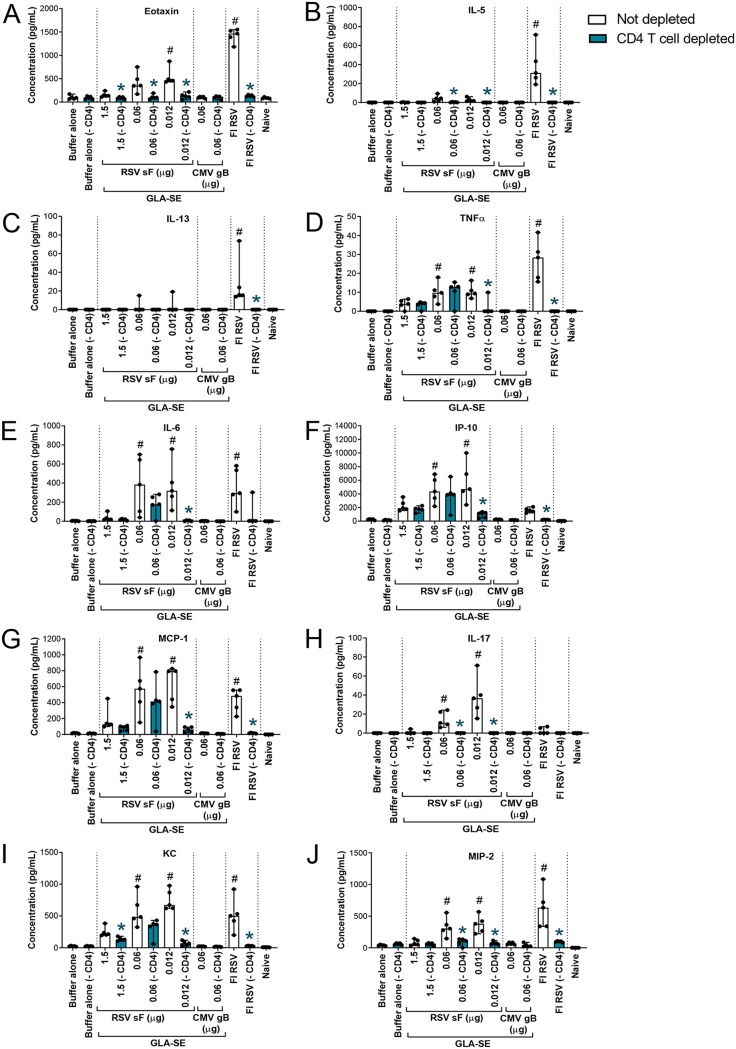
FIG 6.
CD4+ T cell depletion has a strong impact on cytokines induced by FI-RSV or low-antigen-dose immunization post-RSV A2 challenge. BALB/c mice (7 weeks old; n, 5 per group) were immunized i.m. at day 0 and day 21 with either buffer alone, different doses of post-F antigen with GLA-SE (2.5 μg GLA in 2% SE) as an adjuvant, or FI-RSV. A negative-control group was immunized with a nonrelevant antigen (CMV gB) with GLA-SE as an adjuvant. Naïve animals were left untreated. At days 29, 32, and 35, animals were treated i.p. with 250 μg of anti-CD4 antibodies. Four days after i.n. challenge with 106 PFU of wild-type (wt) RSV A2, animals were sacrificed. Lungs were homogenized and clarified, and individual supernatants were analyzed by multiplex assays to assess the respective concentrations of eotaxin (A), IL-5 (B), IL-13 (C), TNF-α (D), IL-6 (E), IP-10 (F), MCP-1 (G), IL-17 (H), KC (I), and MIP-2 (J). Individual results and medians with ranges are presented. Kruskal-Wallis analysis followed by Dunn’s multiple-comparison tests were used for statistical analyses. Symbols indicate an adjusted P value of <0.05 for nondepleted conditions compared to buffer alone (#) or a P value of <0.05 for pairwise Mann-Whitney tests of nondepleted versus CD4 T cell-depleted conditions (*).