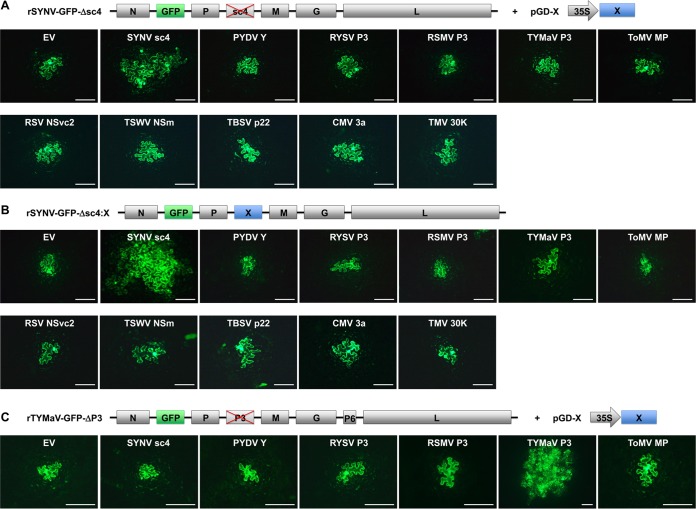
FIG 2.
Inabilities of heterologous MPs to complement the movement of the rSYNV and rTYMaV MP deletion mutants. (A) trans-Complementation of the cell-to-cell movement of rSYNV-GFP-Δsc4 by transiently expressed MPs. Leaves of N. benthamiana plants were agroinfiltrated with bacterial mixtures carrying plasmids required for recovery of rSYNV-GFP-Δsc4 (see Materials and Methods for details) and a binary vector (pGD-X) designated to express individual viral MPs and empty vector (EV) control, as indicated on the panels. (B) Cell-to-cell movement of rSYNV-GFP-Δsc4 derivatives expressing heterologous MPs. The MP genes were each substituted for the sc4 gene in rSYNV-GFP genome, and the resulting rSYNV chimeras were recovered in N. benthamiana leaves after agroinfiltration and monitored for cell-to-cell movement. (C) trans-Complementation of rTYMaV-GFP-ΔP3 movement by transiently expressed MPs in experiments similar to those described in panel A. Genome structures of rSYNV-GFP and rTYMaV-GFP MP deletion mutants and expression strategies of viral MPs are diagramed on the top of each panel. (A to C) GFP fluorescence in infiltrated leaf epidermal cells was photographed with a fluorescence microscope at 12, 15, and 8 dpi, respectively. Scale bars = 200 μm.