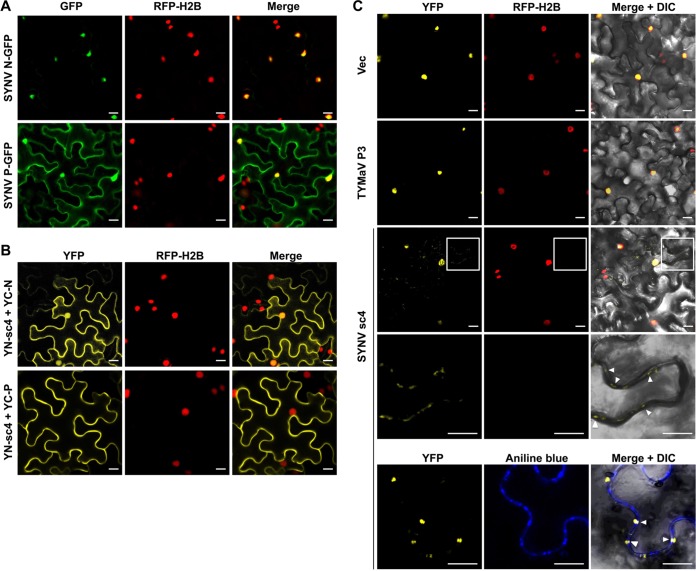
FIG 5.
Relocalization of SYNV N-P complexes from the nuclei to the cell periphery by specific interactions with sc4. (A). Confocal micrographs of SYNV N-GFP and P-GFP fusions expressed after agroinfiltration of leaf epidermal cells of H2B-RFP transgenic N. benthamiana. (B). Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assays to determine interactions between the sc4 and the N or P proteins. Leaf epidermal cells of N. benthamiana RFP-H2B transgenic plants were agroinfiltrated to express the YFP N-terminal-fusion to sc4 (YN-sc4) together with YFP C-terminal-fusions to N (YC-N) or P (YC-P). Confocal micrographs of YFP (BiFC), RFP-H2B, and the merged channel are shown. (C). Localization of SYNV N-P BiFC signals in the absence or presence of sc4. YC-N and YN-P fusions were coexpressed with either an empty vector control, TYMaV P3, or SYNV sc4 in transgenic RFP-H2B N. benthamiana epidermal cells. Note that the fourth row shows higher magnifications of the boxed areas to highlight the punctate BiFC foci along the cell wall (indicated by white arrowheads). In the bottom row, the infiltrated leaf tissues were stained with aniline blue fluorochrome to show colocalization of N-P BiFC signals with the PD, as indicated by the white arrowheads. A differential interference contrast (DIC) channel was included in the merged micrograph to illustrate the cell outline. (A to C) Scale bars = 20 μm.