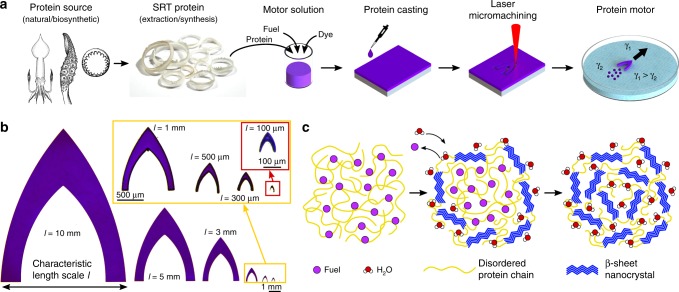
Fig. 1.
Self-propelled protein motors. a Fabrication of protein motors: production of the protein either from natural or biosynthetic sources (adapted from reference with permission54), SRT extraction and purification, preparation of the motor solution (with SRT protein, fuel, and dyes), protein film casting, laser micromachining of the motors to the specified design shape, and self-propulsion by Marangoni forces at the air–liquid interface. b Fabricated protein motor top-view images with characteristic length scales from 10 mm down to 100 μm. c Propulsion mechanism: HFIP fuel is initially trapped in the protein matrix, and it is released to the swimming medium when the motor comes in contact with water. Trapped HFIP molecules are replaced by water, inducing the formation of β-sheet nanostructures