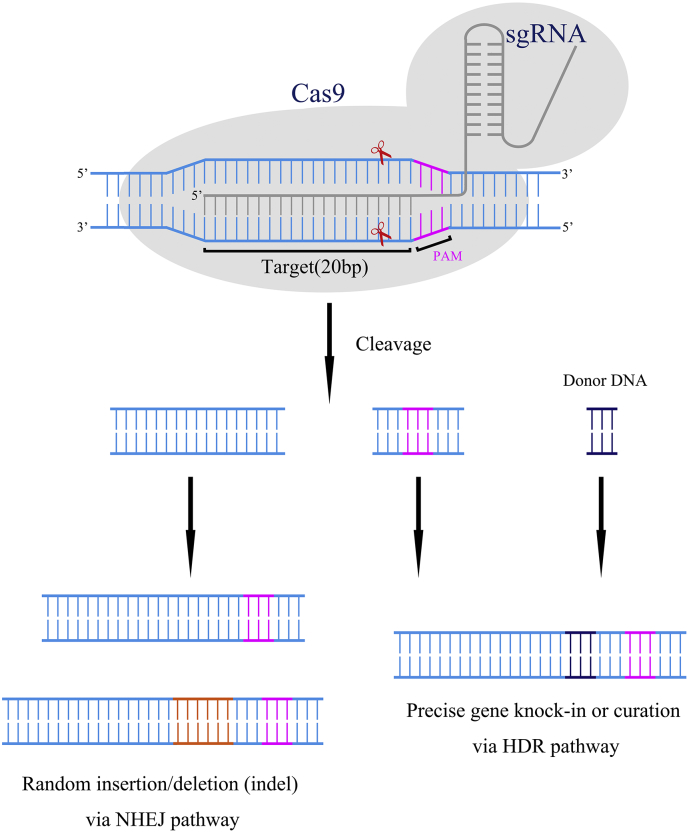
Fig. 1.
Mechanism of the CRISPR-Cas9 targeting system.
1. A sgRNA matches and binds to a 20-nt DNA sequence immediately upstream of an NGG DNA motif (Protospacer-Associated Motif, PAM).
2. The Cas9 protein is guided to the loci by the sgRNA and cuts both strands 3 bp upstream of the NGG.
3. The double-stranded DNA breaks activate the cellular DNA repair machinery, resulting in nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) or homology-directed repair (HDR).