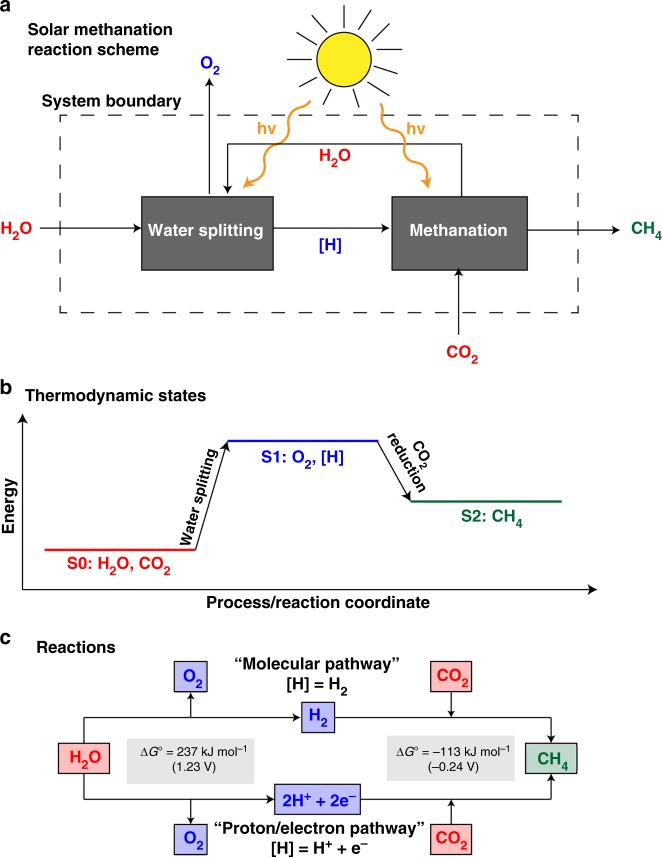
Fig. 2.
Graphical representation of solar methanation reaction schemes and energetics. a In a first reaction step, water is split into reducing equivalents [H] and O2. [H] can be molecular H2 or a H+/e− pair. If [H] is molecular H2, then CO2 is reduced to CH4 via the “molecular pathway”. If [H] is a H+/e− pair, then CO2 is reduced to CH4 via the “proton/electron pathway”. b Graphical representation of the thermodynamic states of the solar methanation reaction. The energy level of the system is elevated from S0 to S1 during the water splitting step. Energy is released during CO2 reduction, reaching the energy level of the products, S2. c Reactions occurring during the solar methanation pathways shown in a. The “molecular” pathway represents the state-of-the-art of industrial methanation, where H2 is produced during water electrolysis, as discussed in the “State-of-the-art industrial CO2 methanation” section