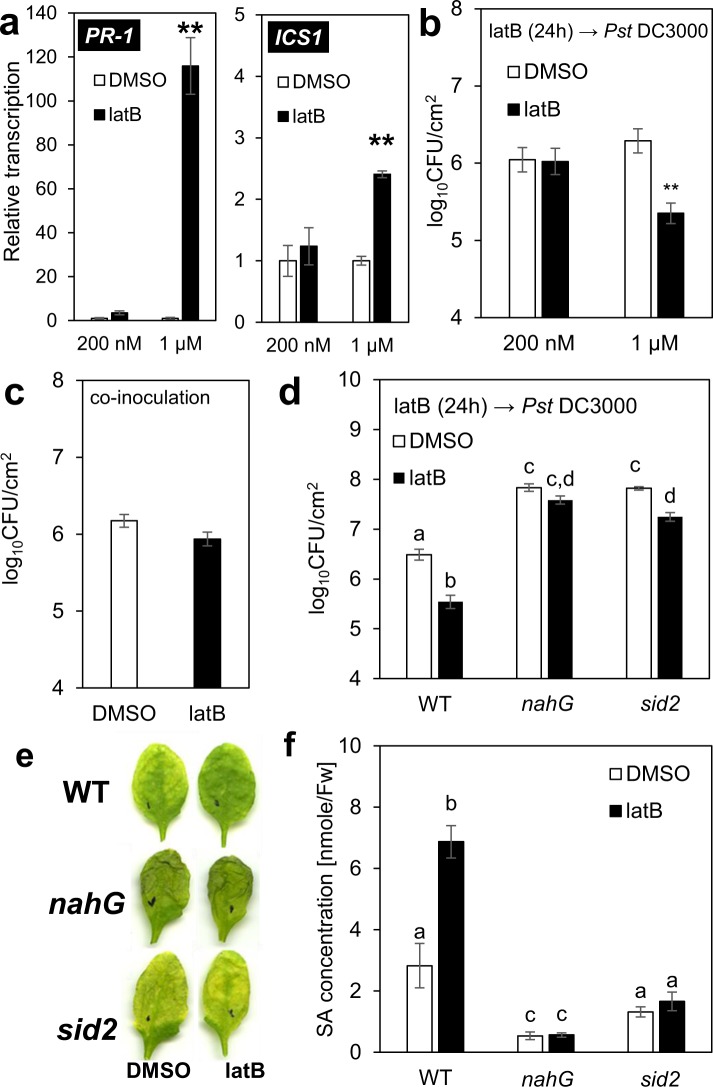
Figure 2.
Four-week-old A. thaliana: Latruculin B-triggered SA pathway is necessary for higher resistance to Pst DC3000 (a). Transcription of SA marker genes PR-1 and ICS1 in four-week-old A. thaliana plants. Plants were treated for 24 h with 200 nM or 1 µM latrunculin B (latB). The transcription level was normalized to the reference gene, TIP41. (b,c) Bacterial titres in four-week-old plants. (b) Plants were pretreated with 200 nM or 1 µM latB for 24 h before inoculation with Pst DC3000. Control plants were pretreated with 0.01 or 0.05% DMSO. (c) Plants were treated with 1 µM latB or 0.05% DMSO, each in a solution containing Pst DC3000. (d) Bacterial titres in four-week-old plants. (e) Representative photographs of adult A. thaliana leaves infected with Pst DC3000 3 days after inoculation. (f) Salicylic acid (SA) concentration after 24 h 1 µM latB treatment. Plants were treated for 24 h with 1 µM latB or 0.05% DMSO before inoculation with Pst DC3000. A. thaliana WT plants (col-0) and mutants with impaired SA pathways (nahG and sid2) were used (d, e, f). Tissue was harvested 3 days after inoculation with Pst DC3000. The values represent mean and error bars (SEM) from four (a,f) and six (b,c,e) independent samples. The asterisks represent statistically significant changes in latB-treated samples compared with controls (**P < 0.01; two tailed Student’s t-test) and statistical differences between the samples (d,f) were assessed using a one-way ANOVA, with a Tukey honestly significant difference (HSD) multiple mean comparison post hoc test. Different letters indicate a significant difference, Tukey HSD, P < 0.01, n = 6.