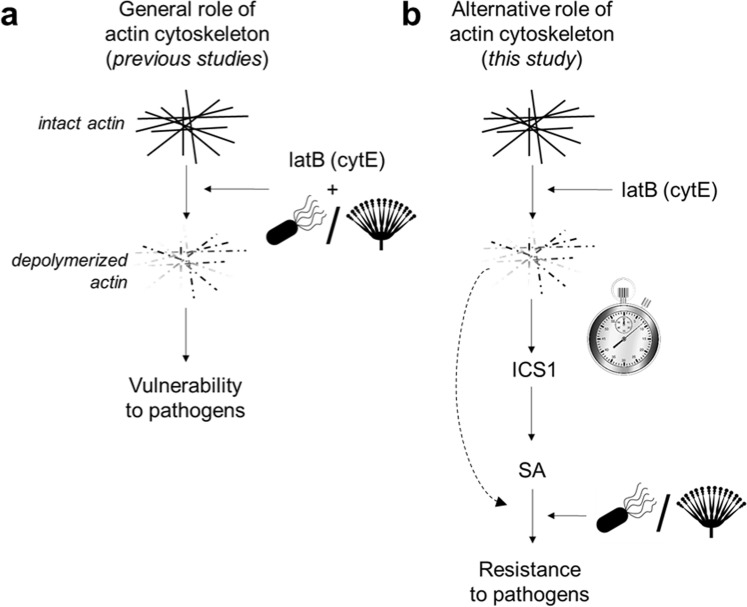
Figure 4.
Possible dual role of actin cytoskeleton in plant response to pathogens. (a) The widely-published scenario in which depolymerization of the actin cytoskeleton by treatment with latrunculin B or cytochalasin E leads to increased plant vulnerability to pathogens. Studies showing this phenomenon co-inoculated plants with a drug and pathogen. (b) The new alternative scenario for the role of the actin cytoskeleton proposed in this manuscript. Plants pretreated with latrunculin B or cytochalasin E before inoculation with a pathogen have time to activate the salicylic acid signalling pathway, resulting in increased resistance to the subsequently inoculated pathogens. latB = latrunculin B; cytE = cytochalasin E; SA = salicylic acid; ICS1 = isochorismate synthase 1; = fungi;
= fungi;  = bacteria.
= bacteria.