FIGURE 5.
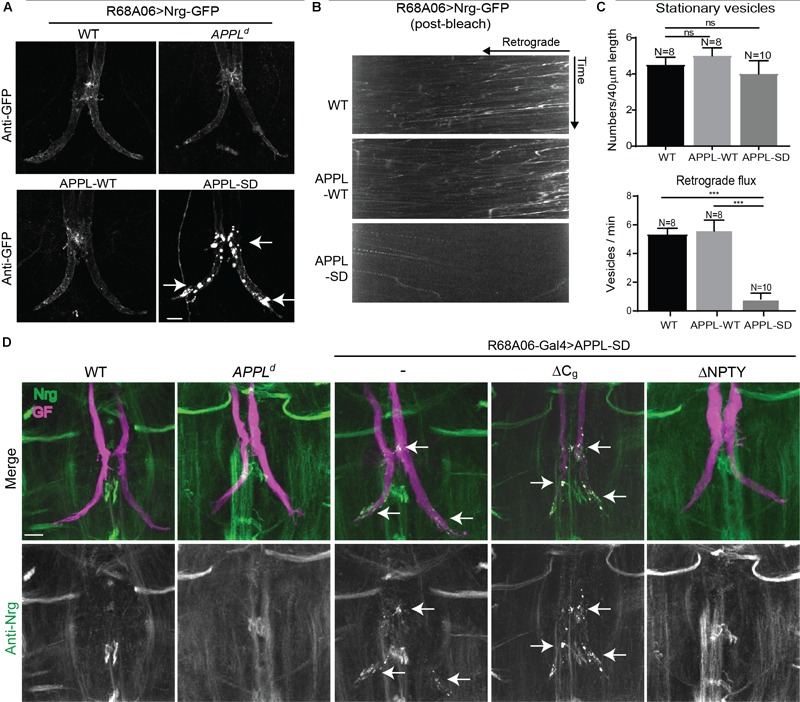
Nrg localization and trafficking in GF terminal of APPL gain and loss of function mutants. (A) Nrg-GFP was conditionally expressed in GFs of wildtype and in APPLd null mutants with the R68A06 Gal4-line as well as co-expressed with wildtype (APPL-WT) and secretion-deficient (APPL-SD) APPL after GF synapse formation. Nrg accumulations in GF terminals are indicated by arrows. Scale bar represents 10 μm. (B) Kymographs of axonal transport of Nrg-GFP vesicles in wildtype (WT) control animals and when co-expressed with APPL-WT or APPL-SD using R68A06 Gal4-line (Supplementary Videos S8–S10). (C) Quantification of Nrg-GFP vesicle trafficking in wildtype background as well as when co-expressed with APPL-WT and APPL-SD. Numbers of stationary vesicles, and numbers of vesicles moving in retrograde direction (Flux) were analyzed. N indicates numbers of axons assessed. Error bars represents standard error mean. Statistical significance between genotypes was assessed using Student’s t-test (ns, non-significant, p > 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001). (D) Localization of endogenous Nrg (green) labeled by an antibody against the intracellular domain of Nrg in wildtype and in APPLd null mutants as well as when with APPL-WT, APPL-SD, APPL-SD-ΔCg, and, APPL-SD-ΔNPTY were expressed in GFs with the R68A06 Gal4-line. GFs were labeled by dye injections of rhodamine-dextran (magenta) into the GF axons. Nrg accumulations in GF terminals are indicated by arrows. Scale bar represents 10 μm.
