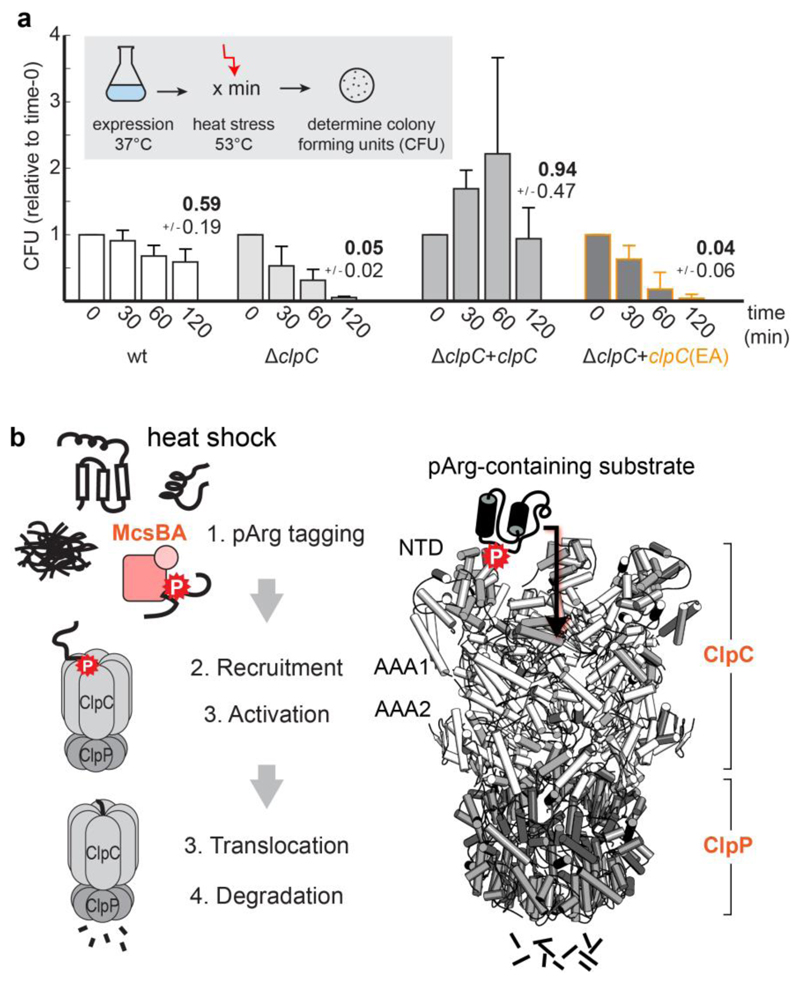
Figure 6. The pArg–ClpCP degradation system.
a, Thermotolerance assay analysing the in vivo complementation of ΔclpC by expressing ClpC and ClpCEA. Levels are normalized to the values before heat shock (time 0), and numbers above bars represent the fraction of cells surviving after 2 h heat shock. CFU, colony-forming units. Error bars show the s.d. of three independent experiments. b, The pArg–ClpCP system. Left, cartoon representation shows that after phosphorylation by the McsB arginine kinase, pArg-tagged proteins are targeted to the ClpCP protease. Binding of pArg proteins to one of the 12 NTD binding pockets stimulates the ATPase activity of ClpC, leading to the translocation of the captured substrate into the ClpP protease cage and to protein degradation. Right, a model of the respective ClpCP complex (ClpC NTD in light grey, ClpC AAA1/2 in white, ClpP in dark grey, substrate in black).