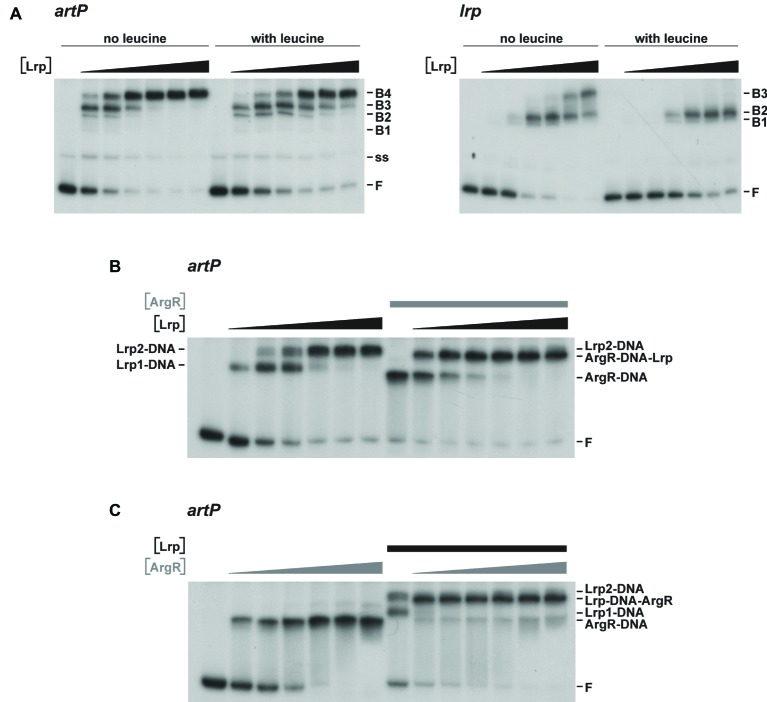
Figure 3.
Representative autoradiographs of EMSAs with Lrp and ArgR binding to radiolabeled fragments bearing the artP or lrp control region in the presence of an excess non-labeled non-specific competitor DNA (sonicated harring sperm DNA). (A) Binding of Lrp to the artP and lrp control region in the absence and in the presence of 7.0 mM l-leucine. The position of free DNA (F), single-stranded DNA (ss) and the various Lrp-DNA complexes (B1 to B4) is indicated. The black triangle represents increasing Lrp concentrations corresponding to 0, 0.23, 0.46, 0.92, 1.84, 3.68, and 7.36 μM (expressed in monomer equivalents). (B) Binding of Lrp and Lrp plus ArgR to the artP control region. In the right-hand part of the panel a constant concentration of ArgR (0.48 nM, expressed in hexamer equivalents and indicated with a gray colored bar) was allowed to bind to the artP control region prior to the addition of increasing concentrations of Lrp (0, 0.23, 0.46, 0.92, 1.84, 3.68, and 7.36 μM indicated with a black colored triangle). The left-hand part of the panel represents binding of the same concentrations of Lrp only, as a control (notice that complexes indicated here as Lrp1 and Lrp2 correspond to complexes B3 and B4 of panel A). (C) In the right-hand part of the panel a constant concentration of Lrp (3.04 μM, indicated with a black colored bar) was allowed to bind to the artP control region prior to the addition of increasing concentrations of ArgR (0, 0.48, 0.96, 1.92, 3.84, 7.68, and 15.3 nM as indicated with a gray colored triangle). The left-hand part of the panel represents binding of the same concentrations of ArgR only, as a control.