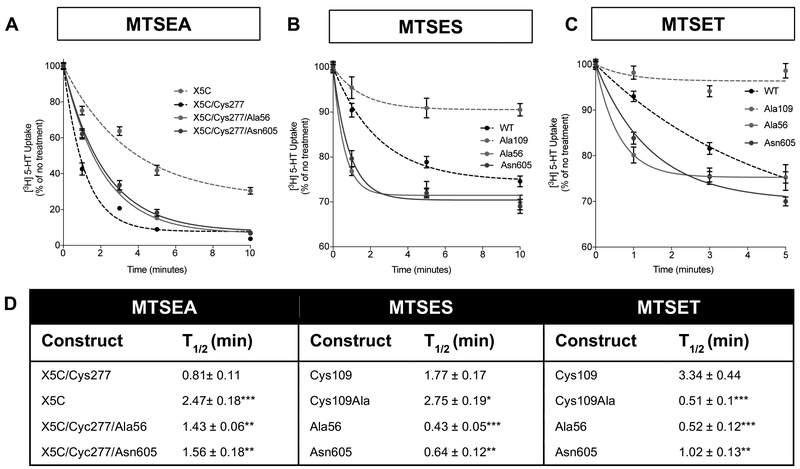
Figure 3: Sensitivity of N and C termini ASD SERT variants to MST inactivation of uptake supports outward-facing conformations.
(A) To determine accessibility of the cytoplasmic permeation pathway HEK-MSR cells expressing terminal ASD-associated mutants (SERT Ala56 and Asn605) in the S277C/X5C background were treated with 2 mM MTSEA for the indicated time. Following treatment, cells were assayed for [3H] 5-HT uptake (50 nM for 10 min at 37°C). Remaining activity is plotted as a percent of untreated cells and the values represent the mean ± SEM from four or more independent experiments. SERT Ala56 and Asn605 were less sensitive to MTSEA inactivation, suggesting that Cys277 was less accessible. (B&C) Cys109, located on the extracellular end of TM1, is an extracellular probe for the membrane impermeant thiol-reactive reagent, MTSES (B) and MTSET (C). Both the terminal ASVs (SERT Ala56 and Asn605) are more sensitive to MTSES and MTSET inactivation, suggesting that Cys109 is more accessible in these mutants compared to control cells. (D) Table with time for MTS reagent to decrease total 5-HT uptake in each mutant by 50% (t1/2). One-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s, *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, n=8.