Figure 1.
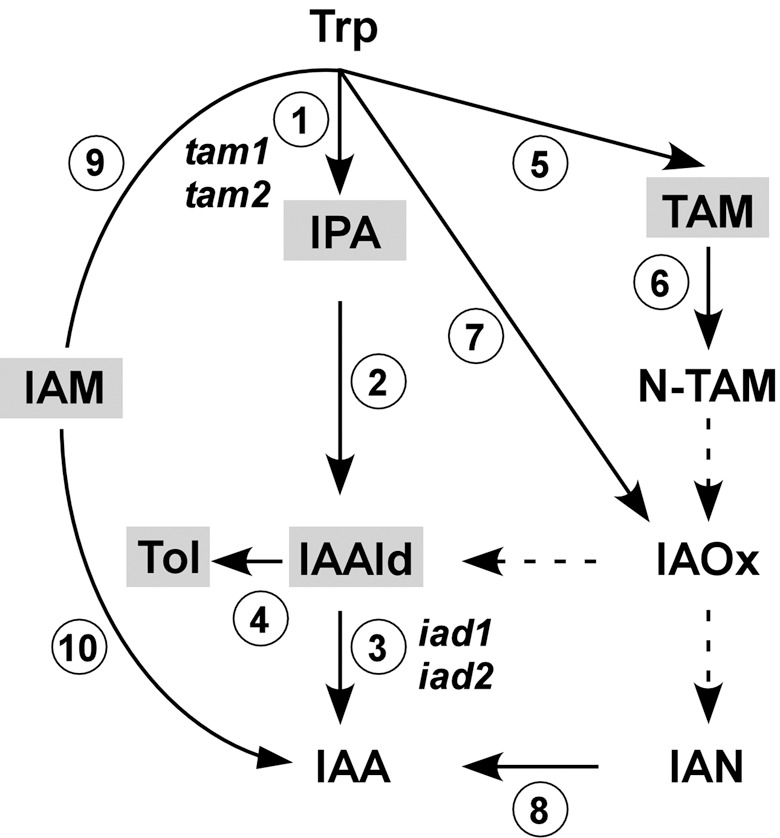
Trp‐dependent IAA biosynthesis. The scheme shows IAA pathways and key intermediates proposed for plants and microorganisms. Trp, tryptophan; IPA, indole‐3‐pyruvic acid; IAAld, indole‐3‐acetaldehyde; IAA, indole‐3‐acetic acid; Tol, indole‐3‐ethanol; TAM, tryptamine; N‐TAM, N‐hydroxyl tryptamine; IAOx, indole‐3‐acetaldoxime; IAN, indole‐3‐acetonitrile; IAM, indole‐3‐acetamide. Enzymes involved in these pathways are: Trp aminotransferase (1), IPA decarboxylase (2), IAAld dehydrogenase (3), IAAld reductase (4), Trp decarboxylase (5), flavin monooxygenase‐like enzymes (6), cytochrome P450 enzymes (7); nitrilase (8); Trp monooxygenase (9); IAM hydrolase (10). Possible intermediates or by‐products of IAA formation thus far reported for fungi are shaded grey (see Discussion). Enzymes for the conversion of intermediates connected by dashed arrows are elusive. U. maydis genes involved in IAA formation are indicated. Tol emerges as a by‐product from IAAld in the absence of IAAld dehydrogenase activity.
