Figure 4.
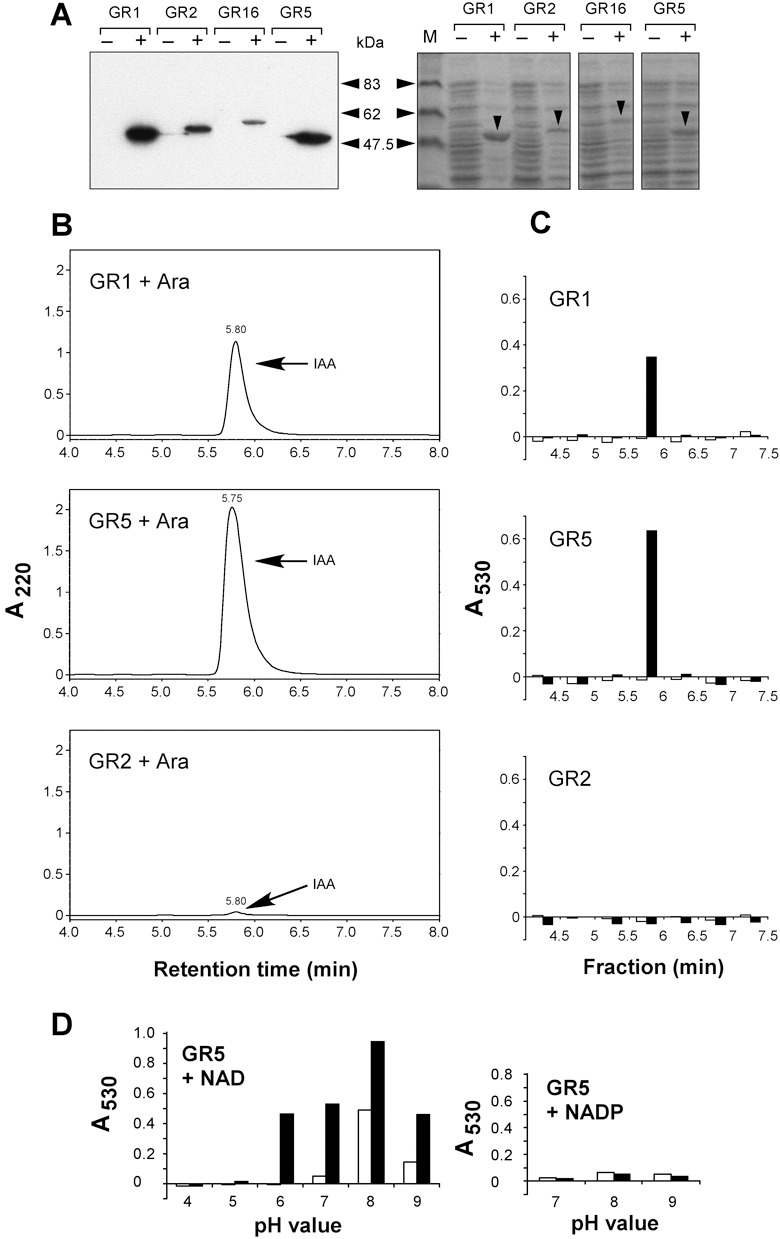
Demonstration of IAAld activity in vitro. (A) Immunoblot analysis of His‐tagged proteins expressed in E. coli strains GR1 (Iad1; 53.7 kDa), GR2 (Pad2; 56.2 kDa), GR16 (Pad16; 57.4 kDa) and GR5 (Iad2; 53.0 kDa) using an anti‐His antibody. Cultures were incubated under non‐inducing (–) or inducing conditions (+). Protein amounts corresponding to 40 µL of cell culture were loaded per lane. Size markers are indicated on the right. The right panel shows the Coomassie‐stained gel loaded with the same amounts of the same protein preparations. Arrowheads point to the Iad1, Pad2, Pad16 and Iad2 proteins expressed under inducing conditions. M: molecular mass standards. (B) HPLC analysis of in vitro reaction products. Identical volumes of enzyme extracts (corresponding to 0.7 mL of cell culture each and 100 µg protein for GR1, 200 µg for GR2 and 400 µg for GR5) prepared from E. coli strains GR1, 2 and 5 grown in parallel under inducing conditions (+Ara) were applied for the enzyme assay in the presence of IAAld (0.5 mm). Reaction products were separated by HPLC. The IAAld substrate (elutes 1 min earlier than IAA under the applied conditions) was removed from the samples via ethyl acetate extraction. Absorbance was monitored at 220 nm. Arrows denote peaks eluting like IAA. (C) Salkowski analysis of HPLC fractions. Fractions from HPLC runs of reaction products under non‐inducing conditions (open bars) and inducing conditions (closed bars) were collected for detection of IAA with the Salkowski reagent. Absorbance was measured at 530 nm. (D) Co‐factor and pH requirements of Iad2. The desalted extract from induced E. coli strain GR5 was incubated with IAAld (0.5 mm) in the presence of either NAD (1 mm) (left panel) or NADP (1 mm) (right panel). Reactions were allowed to proceed for 5 min (open bars) or 30 min (closed bars). Products were treated with the Salkowski reagent. Absorbance was measured at 530 nm.
