Figure 6.
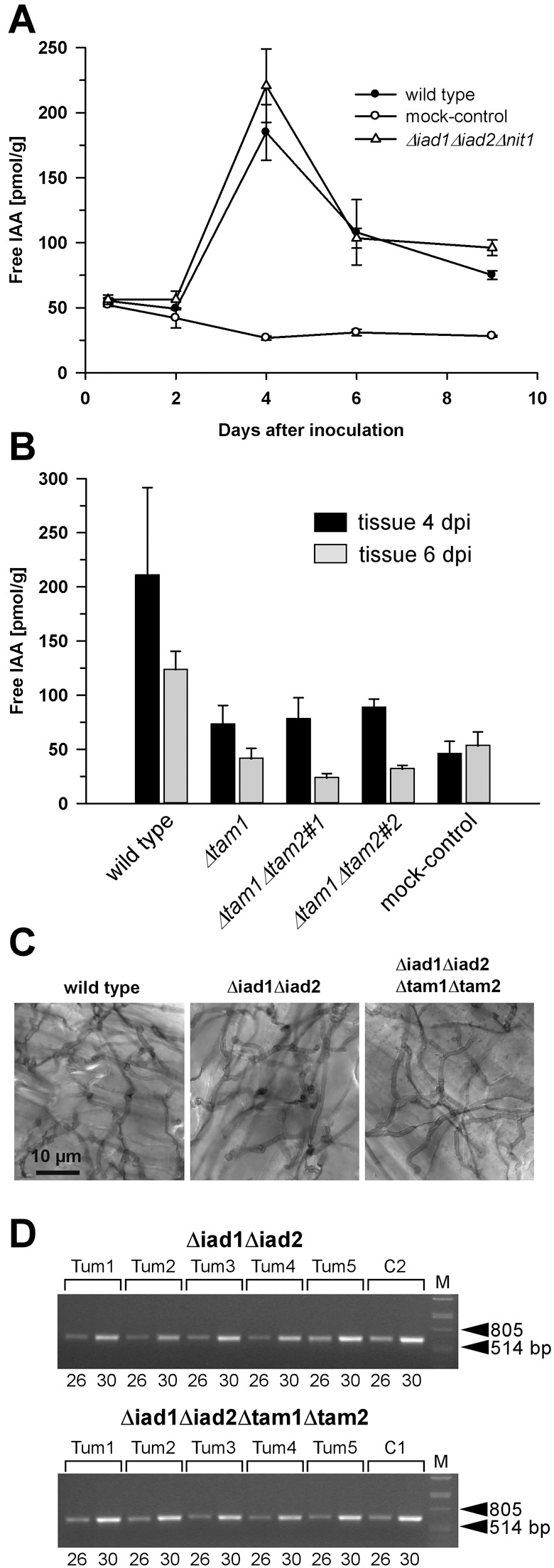
Determination of free IAA levels in maize tissue in response to U. maydis infection and analysis of proliferation of Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1Δtam2 mutants in planta. (A) Plants (6 days old) were inoculated with either combinations of FB1/FB2 strains (wild‐type; •), BH7/BH13 strains (Δiad1Δiad2Δnit1; Δ), or injected with water (mock‐control;  ). (B) Plants were inoculated with either combinations of FB1/FB2 strains (wild‐type), FB1Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1/FB2Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1 strains (Δtam1), two independent combinations of FB1Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1Δtam2/FB2Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1Δtam2 strains (Δtam1Δtam2), or injected with water (mock‐control). (A,B) Concentrations of IAA are calculated in pmol/g fresh weight. Average values and standard deviations of three data points are given. Leaf material was collected at the time points indicated. For the 12‐h and 48‐h time points, material was collected 0.5–3 cm above ground and 0.5–3 cm below the injection site, respectively. For the 4‐, 6‐ and 9‐day time points, chlorotic or early leaf tumour (4 days) and leaf tumour (6 and 9 days) tissue was collected between the ligule and > 1 cm below the injection site. All parts were exclusively from the third and fourth leaves. Non‐infected control material was isolated correspondingly. For each time point, ten or more tissue samples were collected. (C) Maize plants were inoculated with either mixtures of FB1/FB2 (wild‐type), FB1Δiad1Δiad2/FB2Δiad1Δiad2 (Δiad1Δiad2) or FB1Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1Δtam2/FB2Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1Δtam2 (Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1Δtam2) strains. Two days after inoculation samples from infected leaf blade tissue were stained with Chlorazol Black E. Note the ramification of hyphae throughout the epidermal layer. The bar (10 µm) refers to all panels. (D) Detection of FB1Δiad1Δiad2/FB2Δiad1Δiad2 (Δiad1Δiad2) and FB1Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1Δtam2/FB2Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1Δtam2 (Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1Δtam2) strain combinations in maize tumours. Chromosomal DNA (100 ng) isolated from each of five individual tumours (Tum1–5) 6 days after inoculation with either of these combinations was used as template for PCR to amplify a fungal‐specific DNA fragment (see Experimental procedures). C1, C2: DNA (100 ng) isolated from the respective strain combinations prior to plant infection was used as template. Twenty‐six and 30 cycles (numbers below the lanes) were performed. The expected size of the amplified fragment is 633 bp. All lanes are from the same gel. Phage lambda (M) DNA (500 ng) digested with PstI was used as size marker.
). (B) Plants were inoculated with either combinations of FB1/FB2 strains (wild‐type), FB1Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1/FB2Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1 strains (Δtam1), two independent combinations of FB1Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1Δtam2/FB2Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1Δtam2 strains (Δtam1Δtam2), or injected with water (mock‐control). (A,B) Concentrations of IAA are calculated in pmol/g fresh weight. Average values and standard deviations of three data points are given. Leaf material was collected at the time points indicated. For the 12‐h and 48‐h time points, material was collected 0.5–3 cm above ground and 0.5–3 cm below the injection site, respectively. For the 4‐, 6‐ and 9‐day time points, chlorotic or early leaf tumour (4 days) and leaf tumour (6 and 9 days) tissue was collected between the ligule and > 1 cm below the injection site. All parts were exclusively from the third and fourth leaves. Non‐infected control material was isolated correspondingly. For each time point, ten or more tissue samples were collected. (C) Maize plants were inoculated with either mixtures of FB1/FB2 (wild‐type), FB1Δiad1Δiad2/FB2Δiad1Δiad2 (Δiad1Δiad2) or FB1Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1Δtam2/FB2Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1Δtam2 (Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1Δtam2) strains. Two days after inoculation samples from infected leaf blade tissue were stained with Chlorazol Black E. Note the ramification of hyphae throughout the epidermal layer. The bar (10 µm) refers to all panels. (D) Detection of FB1Δiad1Δiad2/FB2Δiad1Δiad2 (Δiad1Δiad2) and FB1Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1Δtam2/FB2Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1Δtam2 (Δiad1Δiad2Δtam1Δtam2) strain combinations in maize tumours. Chromosomal DNA (100 ng) isolated from each of five individual tumours (Tum1–5) 6 days after inoculation with either of these combinations was used as template for PCR to amplify a fungal‐specific DNA fragment (see Experimental procedures). C1, C2: DNA (100 ng) isolated from the respective strain combinations prior to plant infection was used as template. Twenty‐six and 30 cycles (numbers below the lanes) were performed. The expected size of the amplified fragment is 633 bp. All lanes are from the same gel. Phage lambda (M) DNA (500 ng) digested with PstI was used as size marker.
