Figure 5.
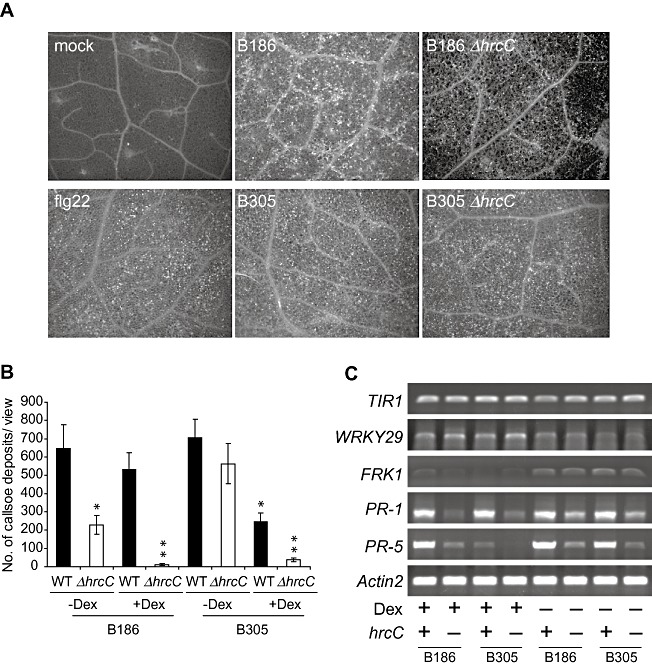
Elicitation of Arabidopsis basal defence responses by Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris (Xcc) is impaired, not elevated, when the hrcC gene is deleted. (A) Representative images of callose deposition in leaves 24 h after infiltration of Arabidopsis Col‐0 leaves with flg22 peptide or with Xcc strains of the indicated genotype. (B) Quantification of callose deposits per field of view 24 h after infiltration of Xcc strains into Arabidopsis Col‐0 plants carrying avrPto under the control of a dexamethasone‐inducible promoter, activated in some samples by dexamethasone application 24 h prior to bacterial inoculation. Top and bottom lines of the x‐axis annotation indicate the bacterial genotype, middle line indicates plant treatment (–Dex, mock treatment; +Dex, with dexamethasone treatment). Mean ± standard error and statistical significance from other plants treated with the same bacterial strain (t‐test, P < 0.05) are shown; asterisk above ΔhrcC—Dex is for difference from wild‐type (WT)—Dex; asterisk above WT +Dex is for difference from WT—Dex; double asterisk above ΔhrcC+Dex is for difference from both ΔhrcC—Dex and WT +Dex. (C) Abundance of the indicated mRNAs 24 h after the treatments described in (B). For hrcC genotypes, + indicates wild‐type hrcC+ and—indicates ΔhrcC. Equivalent tissue quantities were extracted and assayed using semiquantitative reverse transcription‐polymerase chain reaction (RT‐PCR); Actin2 served as a control for mRNA equivalence.
