Figure 1.
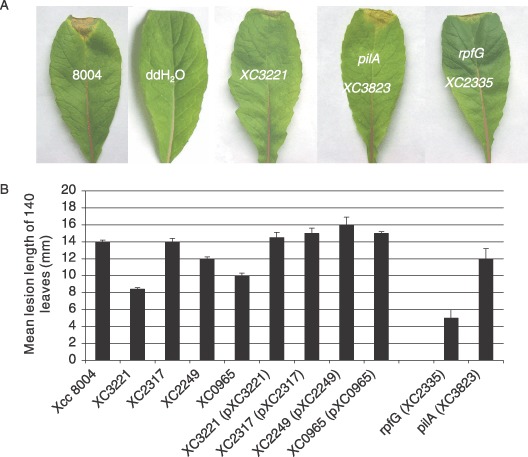
The effects of mutation of genes encoding the PilZ domain proteins XC0965, XC2249, XC2317 and XC3221 on the virulence of Xcc to Chinese radish. The virulence of each mutant was tested by measurement of the lesion length after bacteria were introduced into the vascular system of Chinese radish by leaf clipping. Values given are the means and SD of 60 measurements. Also shown are the effects of mutation of rpfG, which encodes an HD‐GYP domain regulatory protein and pilA encoding the major pilin. (A) Representative virulence assays for (from left to right) Xcc wild‐type strain 8004, negative control (H2O), XC3221::Tn5gusA5 mutant, pilA mutant (XC3823::Tn5gusA5) and rpfG deletion mutant. (B) Mutation of XC3221, XC2249 and XC0965 gave a significant reduction in virulence in repeated tests, although mutation of XC2317 had no effect. Introduction of the cloned genes restores virulence of these mutants to wild‐type levels, but had no influence on the XC2317 mutant, which retained wild‐type virulence.
