Figure 3.
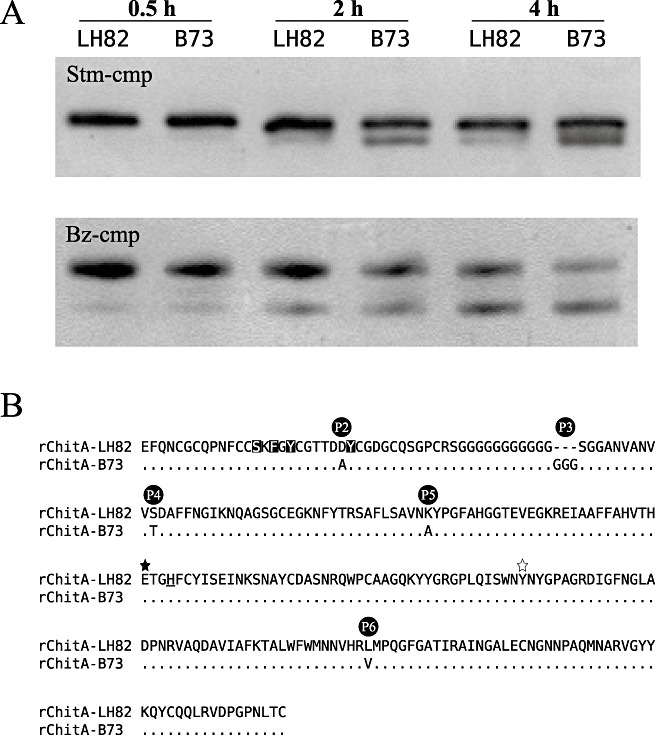
Modification of rChitA alloforms by fungal chitinase‐modifying proteins (cmps). (A) rChitA‐LH82 and rChitA‐B73 were incubated with either Stm‐cmp‐containing protein extracts from Stenocarpella maydis (top gel) or purified Bz‐cmp (cmp from Bipolaris zeicola) (bottom gel). Aliquots from each of the four reactions were taken at 0.5, 2 and 4 h. (B) Sequence alignment of the two rChitA alloforms. The five differences between the proteins are labelled P2 to P6. The rChitA‐LH82 sequence is shown in the top row; the rChitA‐B73 sequence is aligned below. Dots indicate homology; dashes indicate gaps; letters indicate amino acid differences. The P1 polymorphism is in the secretion signal sequence of ChitA and is not present in rChitA. The serine, phenylalanine and two tyrosine amino acids that are inverted are predicted to be involved in chitin binding (Aboitiz et al., 2004). The filled star marks a glutamic acid that is predicted to be essential for catalysis; the open star marks a tyrosine that probably forms part of the active site of the enzyme (Verburg et al., 1992). The underlined histidine marks the end of exon 1 and the start of exon 2 (Fig. 1A).
