Figure 1.
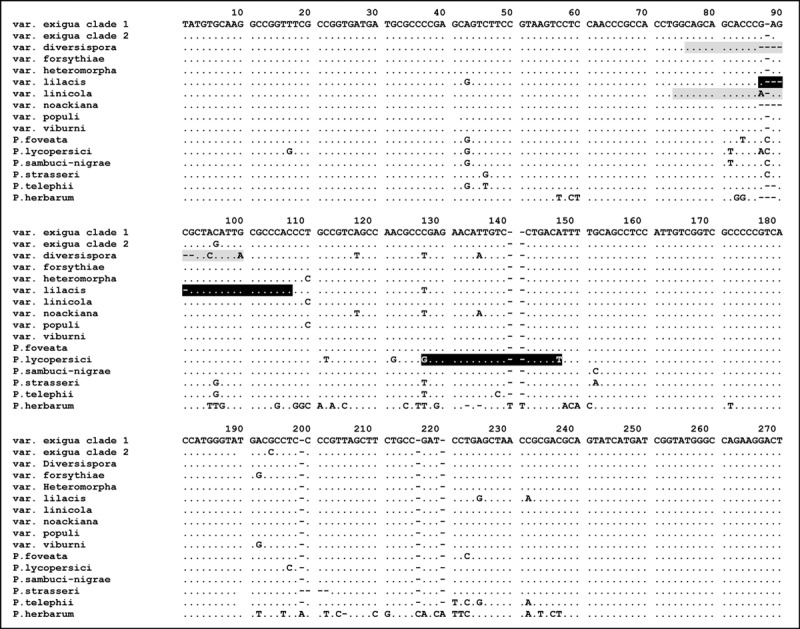
Alignment of actin sequences of 13 Phoma strains belonging to the P. exigua complex and three outgroup species. Strains included are P. exigua var. exigua (CBS 431.74 and CBS 101156), var. diversispora (CBS 531.86), var. forsythiae (CBS 101213), var. heteromorpha (CBS 443.94), var. lilacis (CBS 569.79), var. linicola (CBS 116.76), var. noackiana (CBS 100353), var. populi (CBS 100167), var. viburni (CBS 100354), P. sambuci‐nigrae (CBS 109170), P. foveata (CBS 341.67), and P. lycopersici (CBS 378.67). As outgroup species, P. strasseri (CBS 261.92), P. telephii (CBS 760.73) and P. herbarum (CBS 615.75) were included. Primers designed for this study are indicated by marked blocks: grey sequence blocks represent a forward primer sequence, black blocks a reverse primer. The full stops indicate characters identical to those in the first line and dashes represent alignment gaps. Primer ACTdiv76F spans var. diversispora nucleotides 76‐100, primer ACTlil103R spans var. lilacis nucleotides 87‐107, primer ACTlin74L spans var. linicola nucleotides 74–90, and primer ACTlyc145R spans P. lycopersici nucleotides 127–147.
