Figure 2.
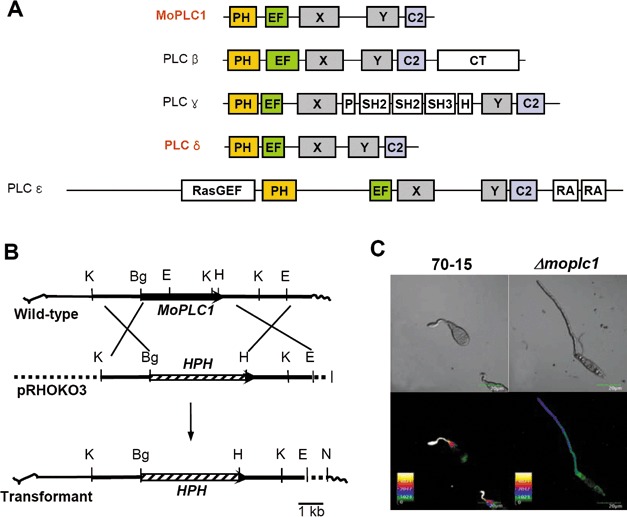
Comparison of domain architecture between Magnaporthe oryzae phospholipase C 1 (MoPLC1) and mammalian phospholipase C (PLC) subtypes, and the effect of deletion of MoPLC1 on calcium fluxes in the fungus. (A) Domain architecture of PLC subtypes. PH, pleckstrin homology domain; EF, EF‐hand domain; X, catalytic X domain; Y, catalytic Y domain; C2, C2 domain; CT, regulatory carboxyl terminus; RasGEF, guanine nucleotide exchange factor domain for Ras‐like small GTPases; RA, Ras association domain; SH, internal Src‐homology domain. (B) Schematic diagram showing the strategy used for targeted deletion of the MoPLC1 gene. K, KpnI; Bg, BglII; H, HindIII; E, EcoRI; N, NotI. (C) Effect of MoPLC1 deletion on calcium fluxes. Germinating conidia on a hydrophobic surface were photographed either under differential interference contrast microscopy (top panels) or confocal microscopy (bottom panels). C, conidium; G, germ tube. Scale bar, 20 µm.
