Figure 2.
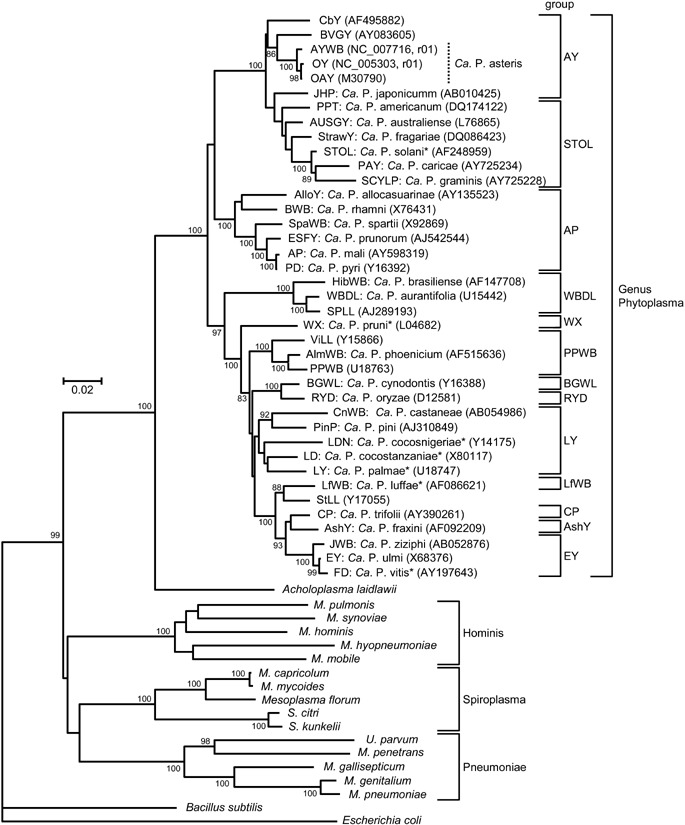
Phytoplasmas comprise a single clade that diverges from Acholeplasma spp. A phylogenetic tree was constructed by the neighbour‐joining method (Saitou and Nei, 1987) using 16S rRNA gene sequences from phytoplasmas, acholeplasma, mycoplasmas, spiroplasmas, Mesoplasma florum, Ureaplasma parvum, Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli (outgroup). Numbers on branches are the bootstrap values (only values > 80% are shown). GenBank accession numbers are given in parentheses. Asterisks indicate the proposed provisional names (IRPCM, 2004). The phylogeny presented here is consistent with IRPCM (2004) and the MolliGen database (http://cbi.labri.fr/outils/molligen/) (Barre et al., 2004). Abbreviations: AlloY, allocasuarina yellows; AlmWB, Almond witches’ broom; AP, apple proliferation; AshY, ash yellows; AUSGY, Australian grapevine yellows; AY, aster yellows; AY‐WB, aster yellows phytoplasma strain witches’ broom; BGWL, Bermuda grass white leaf; BVGY, Buckland valley grapevine yellows; BWB, buckthorn witches’ broom; Ca. P., Candidatus Phytoplasma; CbY, Chinaberry yellows; CnWB, chestnut witches’ broom; CP, clover proliferation; ESFY, European stone fruit yellows; EY, elm yellows; FD, flavescence dorée of grapevine; HibWB, Hibiscus witches’ broom; JHP, Japanese Hydrangea phyllody; JWB, jujube witches’ broom; LD, coconut lethal yellowing; LDN, coconut lethal yellowing; LY, coconut lethal yellowing; LfWB, loofah witches’ broom; M., Mycoplasma; OY, onion yellows; PAY, papaya; PD, pear decline; PPT, potato purple top wilt; PPWB, Caribbean pigeon pea witches’ broom; RYD, rice yellow dwarf; S., Spiroplasma; SCYLP, sugarcane yellow leaf syndrome; SpaWB, spartium witches’ broom; SPLL, sweet potato little leaf; STOL, stolbur; StrawY, strawberry yellows; ViLL, Vigna little leaf; WBDL, witches’ broom disease of lime; WX, western X‐disease.
