Figure 1.
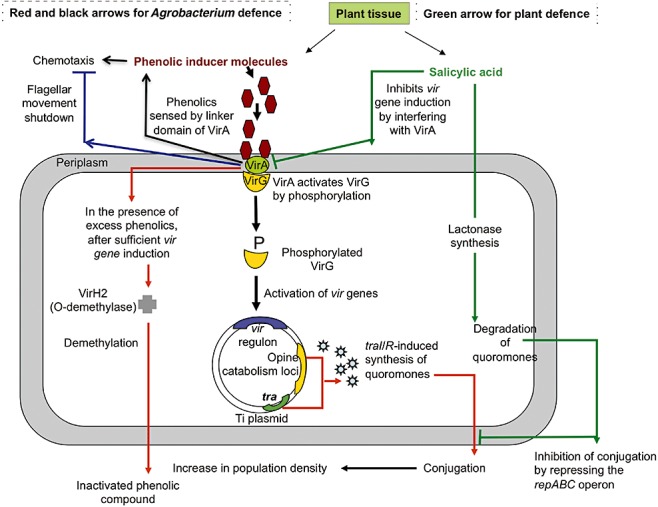
Phenolics in the Agrobacterium–plant interaction. Black arrows indicate how Agrobacterium uses phenolics to initiate pathogenesis in host plants for opine synthesis and nutrition, and red arrows indicate how it inactivates the excess amounts of the same phenolics using its own specific O‐demethylase system. Blue arrow indicates the involvement of the phenolic‐sensing bacterial VirA protein in negative chemotaxis. Green arrows show how plants synthesize and use some phenolics, such as salicylic acid, to interfere with VirA and hence pathogenesis, and also to degrade the quoromones that give ecological advantage to Agrobacterium over other bacteria in competition for the opines synthesized by the infected plant.
