Figure 4.
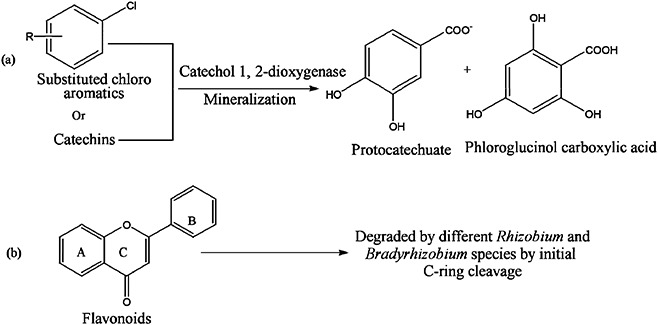
Reactions showing how rhizospheric phenolics are utilized as sources of carbon and energy by Rhizobium spp. for saprophytic and symbiotic survival in soil and host. (a) Mineralization of catechins and substituted chloro‐aromatics by catechol‐1,2‐dioxygenase into phloroglucinolcarboxylic acid and protocatechuate. (b) Degradation of flavonoids by C‐ring cleavage into utilizable forms.
