Figure 3.
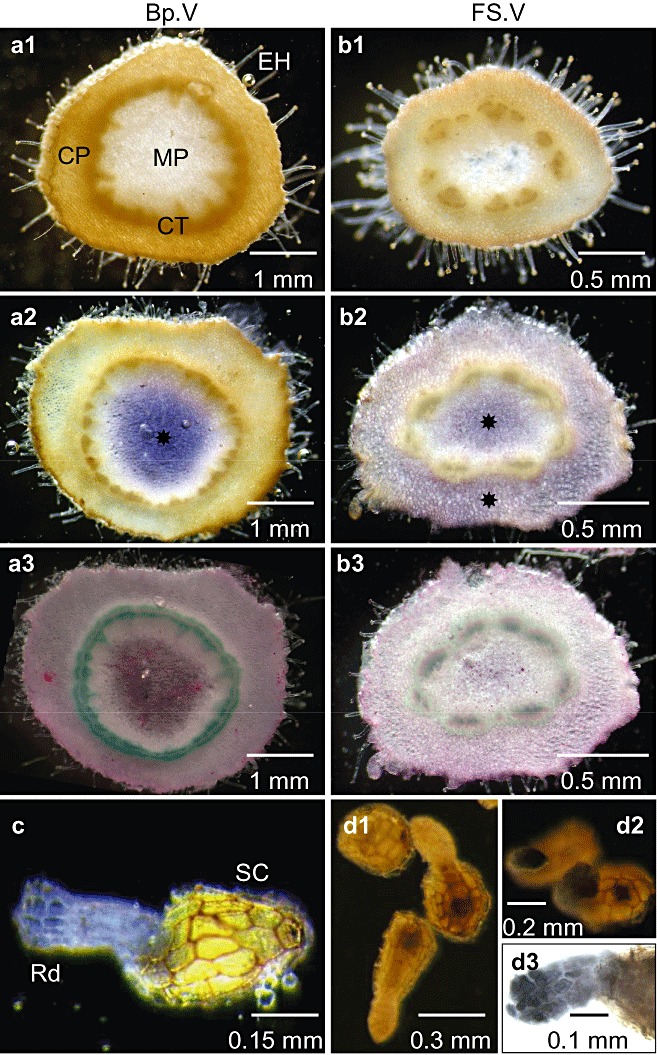
Tissue localization of soluble acid invertase (SAI) activity in seeds and flowering shoots of Phelipanche ramosa parasitizing tomato plants. (a1, b1) Control cross‐sections of basal (Fp.V) and apical (FS.V) shoots incubated after fixation in reaction medium without sucrose. (a2, b2) Assay sections incubated after fixation in a reaction mixture containing sucrose. SAI activity ( ) is shown in blue in medullar and cortical parenchyma. No cell wall invertase (CWI) activity was detected on unfixed sections (data not shown). Staining on fixed sections was thus attributed to SAI. (a3, b3) Post‐activity staining of cellulosic (purple) and lignified (green) tissues using Mirande's reagent. (c) Germinated seeds incubated in the reaction mixture containing sucrose. (d1) NTB staining of seeds without sucrose in reaction medium. (d2) NTB staining of seeds with sucrose in reaction medium. (d3) Zoom of the radicle region stained with NTB: accumulation of reducing sugars produced from SAI‐mediated hydrolysis of sucrose is shown in black in the apex of the radicle. CP, cortical parenchyma; CT, conductive tissues; EH, epidermal hairs; MP, medullar parenchyma; NTB, nitrotetrazolium blue; Rd, radicle; SC, seed coat.
) is shown in blue in medullar and cortical parenchyma. No cell wall invertase (CWI) activity was detected on unfixed sections (data not shown). Staining on fixed sections was thus attributed to SAI. (a3, b3) Post‐activity staining of cellulosic (purple) and lignified (green) tissues using Mirande's reagent. (c) Germinated seeds incubated in the reaction mixture containing sucrose. (d1) NTB staining of seeds without sucrose in reaction medium. (d2) NTB staining of seeds with sucrose in reaction medium. (d3) Zoom of the radicle region stained with NTB: accumulation of reducing sugars produced from SAI‐mediated hydrolysis of sucrose is shown in black in the apex of the radicle. CP, cortical parenchyma; CT, conductive tissues; EH, epidermal hairs; MP, medullar parenchyma; NTB, nitrotetrazolium blue; Rd, radicle; SC, seed coat.
