Figure 1.
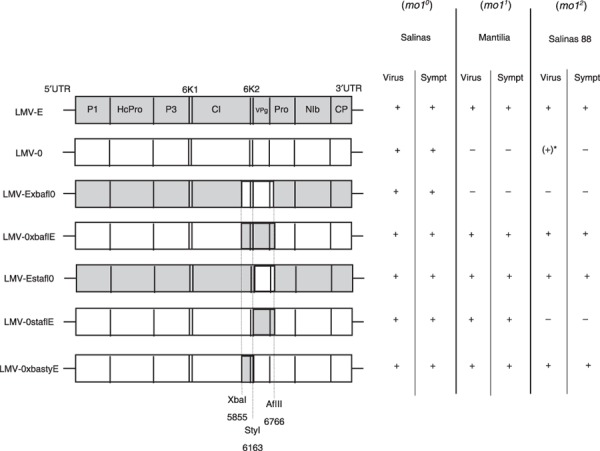
Structure and biological properties of susceptible and resistant lettuce plants of the Lettuce mosaic virus (LMV) recombinants used in this study. Left: schematic representations of the genomes of the recombinants constructed between LMV‐0 and LMV‐E. Coding sequences of LMV‐0 and LMV‐E are represented by white and grey boxes, respectively. Restriction sites used to construct the recombinants and their position along the LMV genome are indicated. Right: behaviour of the parental LMV isolates and of the recombinants in susceptible (mo10, cultivar Salinas) or resistant (mo11, cultivar Mantilia; mo1 2, cultivar Salinas 88) lettuce plants. Virus, viral accumulation in systemically infected leaves; Sympt, symptoms; –, no viral accumulation or no symptoms; +, viral accumulation or symptoms. *(+) denotes sporadic detection of low‐level (80% less than in susceptible plants), symptomless, systemic LMV‐0 accumulation in some Salinas 88 plants.
