Figure 1.
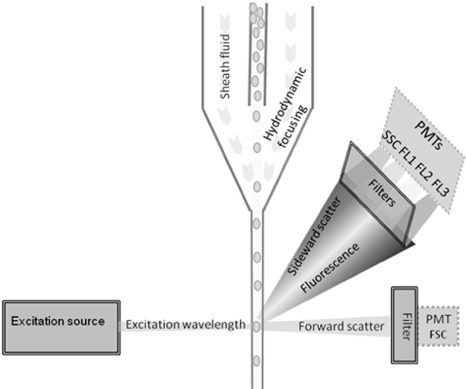
Conceptual figure of a flow cytometer, showing the fluidics system (solid lines), optical system (double lines) and electronics system (dotted lines). The fluidics system delivers the particles of the sample in a single file to the flow cuvette. This is done by injecting the sample into a sheath fluid, that narrows down the sample stream into a single cell line by hydrodynamic focusing. The optical system consists of one or more excitation sources (laser, lamp or light emitting diode) to excite the cells in the flow cuvette. A set of filters and mirrors deflects and passes certain wavelengths of the emitted fluorescence (FL1‐3) and scattered laser light (SSC and FSC). The key parts of the electronics system are the photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) that detect the incoming photons, multiply the current they produce and send this electric signal to the computer where it is displayed as single‐parameter histogram or two‐parameter dot plot.
