Figure 1.
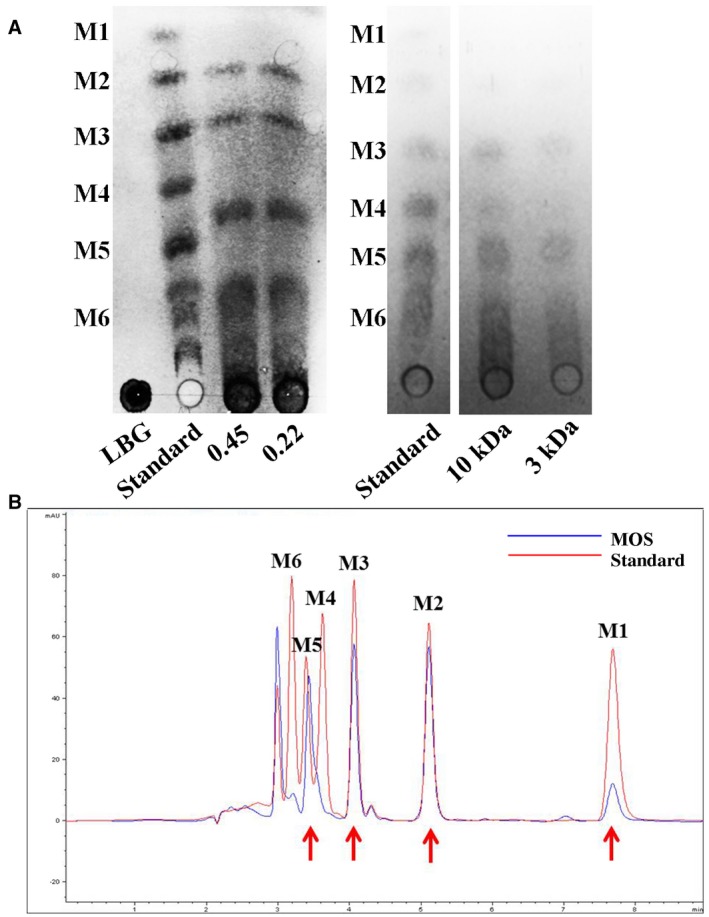
Purification (A) and sugar composition analysis (B) of MOS. (A) TLC showed that polysaccharide‐free hydrolysis products were obtained through centrifugation‐microfiltration‐ultrafiltration steps. Purified BpMan5 was incubated with 10 mg/mL LBG for 24 h at 50 °C. The hydrolysis products were purified successively through centrifugation, microfiltration, and ultrafiltration, and finally detected using TLC. Mobile phase: mixed liquor of ethyl acetate, acetic acid, ethanol, and water (12:3:3:1, v/v). M1, mannose; M2, mannobiose; M3, mannotriose; M4, mannotetrose; M5, mannopentaose; M6, mannohexaose; LBG, locust bean gum; standard: a standard mixture of mannose (M1) to mannohexaose (M6); 0.45, microfiltration using 0.45 μm microfiltration filter membrane; 0.22, microfiltration using 0.22 μm microfiltration filter membrane; 10 kDa, ultrafiltration using 10 kDa tubular ultrafiltration; 3 kDa, ultrafiltration using 3 kDa tubular ultrafiltration. The red circle indicates that the polysaccharides can be ultimately removed through 3 kDa tubular ultrafiltration. (B) HPLC analysis confirmed that the MOS mixture was mainly composed of mannobiose, mannotriose, and mannopentaose. MOS mixtures were first labelled with PMP and then loaded into an Agilent 1200 series LC system equipped with a C18 reverse column. Mobile phase: 0.1 M NH4OAc and acetonitrile at a ratio of 78:22. Flow rate: 1 mL/min. Standard: a standard mixture of mannose (M1) to mannohexaose (M6).
