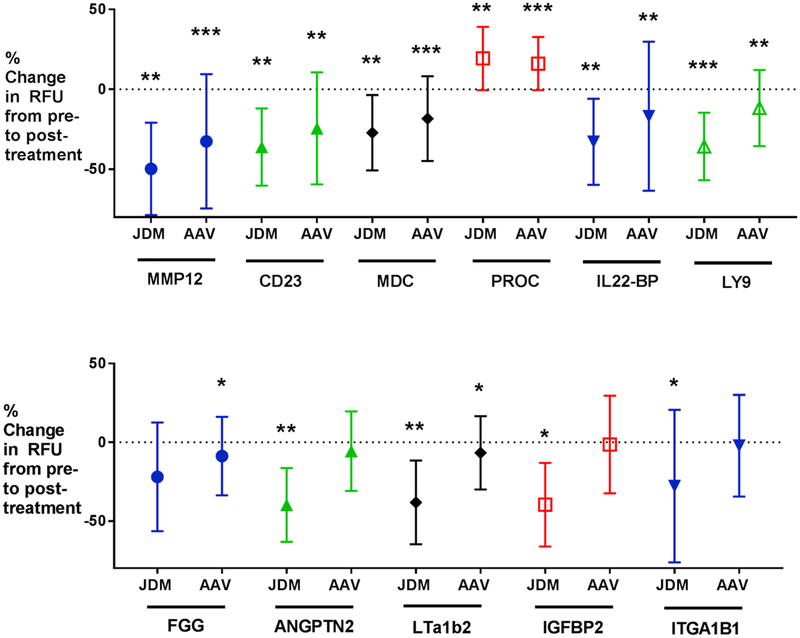
Fig. 1.
Shown are plots of mean change in Relative Fluorescence Units (RFU’s) from baseline and standard deviation for 11 efficacy biomarkers in AAV and JDM. Significance is noted as follows: *P-value ≤0.05; **P-value ≤0.01; ***P-value ≤0.001. Eight of 11 biomarkers reached significance in AAV; 10 of 11 reached significance in JDM (by paired t-test). All biomarkers were decreased by glucocorticoids, except for Protein C. These changes were in the same direction as seen in previous studies in IBD and DMD [13,14]. Abbreviations: AAV = anti-neutrophil antibody-associated vasculitis; JDM = juvenile dermatomyositis; IBD = Inflammatory Bowel Disease; DMD = Duchenne muscular dystrophy; MMP-12 = matrix metalloproteinase-12; MDC = macrophage derived cytokine; PROC = Protein C; IL22-BP = IL22 binding protein; LY9 = T lymphocyte antigen Ly9; FGG = fibrinogen gamma chain; ANGPT2 = angiopoietin-2; IGFBP-2 = insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2; ITGA1 ITGB1 = integrin A1 B1.