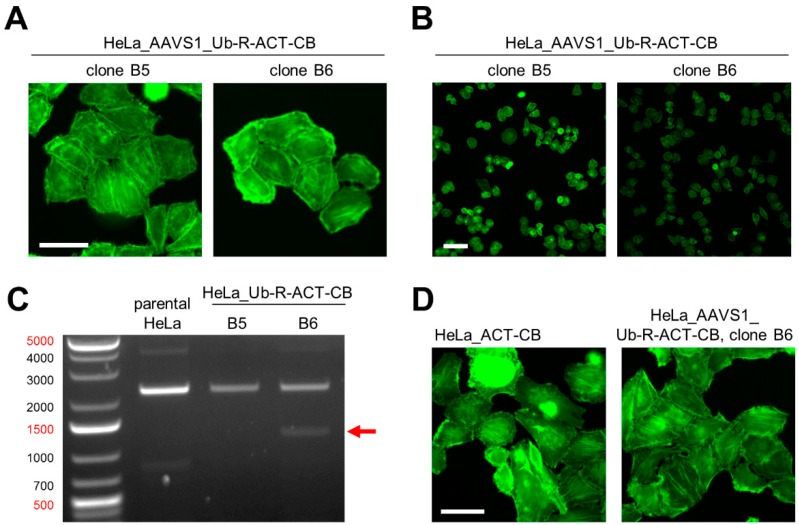
Figure 5.
Generation of a HeLa cell line expressing Ub-R-ACT-CB stably integrated into the AAVS1 locus by using CRISPR/Cas9 technology. (A) Fluorescence images of two CRISPR-engineered HeLa cell clones expressing ACT-CB, scale bar: 50 µM. (B) Comparison of fluorescence intensity between HeLa_AAVS1_Ub-R-ACT-CB clone B5 and B6, scale bar: 100 µm. (C) PCR-based genotyping of HeLa_AAVS1_Ub-R-BC1-CB clones B5 and B6 in comparison to parental HeLa cells. Genomic DNA of the monoclonal cells was extracted and subjected to PCR using the genotyping strategy illustrated in Figure 4B. Shown are the resulting PCR products (indicated by arrow) on a 1% agarose gel stained with ethidiumbromid. (D) Representative fluorescence images of living HeLa cells stably expressing the respective ACT-CB. Left image illustrates HeLa_ACT-CB cells generated by random integration of the non-modified ACT-CB. The right image shows HeLa_AAVS1_Ub-R-ACT-CB cells generated by site-directed integration of the ubiquitin-modified ACT-CB using CRISPR/Cas9 technology, scale bar: 50 µm.