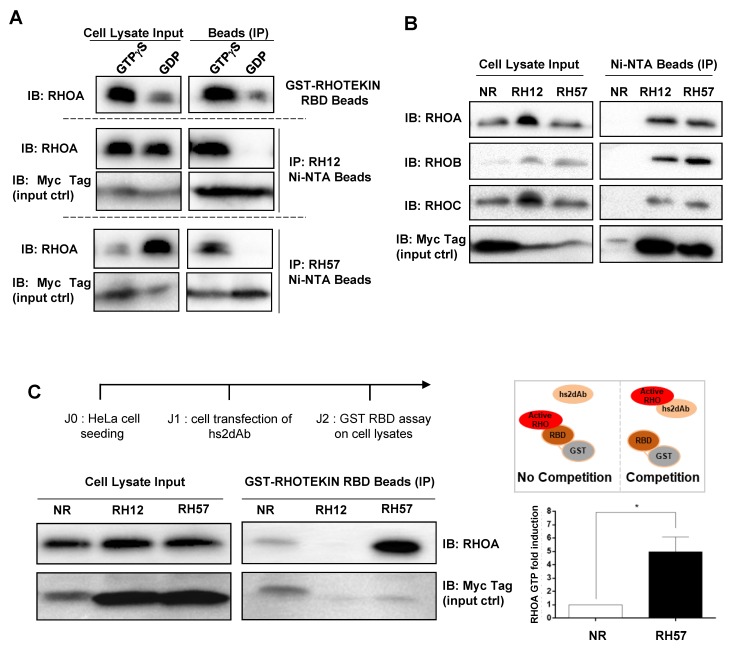
Figure 3.
Intracellular antibody characterization of RH57 hs2dAb. (A) The hs2dabs RH12 and RH57 were expressed in HeLa cells with a 6xhis and carboxy Myc tag and the endogenous RHO GTPases were loaded with either GTPγS or GDP in the cell lysate. The intracellular antibodies were immuno-precipitated with Capture Select His tag affinity beads and an anti-RHOA antibody was used to monitor which pool of RHO (GTP or GDP) was bound by the intracellular antibodies. The recovered intracellular antibodies were monitored by immuno-blotting with anti-Myc tag. The GST-RHOTEKIN RHO binding domain (RBD), which allows to pull down GTP-bound RHO proteins on glutathione beads, was used as positive control. (B) Intracellular antibody immuno-precipitation assays on endogenous RHO proteins. Assays were performed as in panel A, but on non-loaded endogenous RHO proteins. The non-related NR hs2dAb was used as a negative control. (C) GST-RHOTEKIN RBD interference assay intracellular antibodies. The hs2dabs NR, RH12, and RH57 were expressed in HeLa cells with a 6xHis and carboxy Myc-tag. Intracellular expression of RH12 impedes the GST-RBD capture of RHOA-GTP. RH57 induced an increase of RHOA-GTP. NR binds to the beads. Representative blot of three independent experiments. Right: scheme of the binding competition events. Quantification of RHOA-GTP fold increase in RH57 conditions compared with the NR condition reveals potential stabilization of RHOA-GTP or GAP inhibition activity by the RH57. Error bars are mean ± SD of the biological repeats. * p < 0.05. IP = immuno-precipitation; IB = immuno-blot.