Figure 2. Recombinant ELP-RBDs efficiently bind and coacervate single stranded RNA.
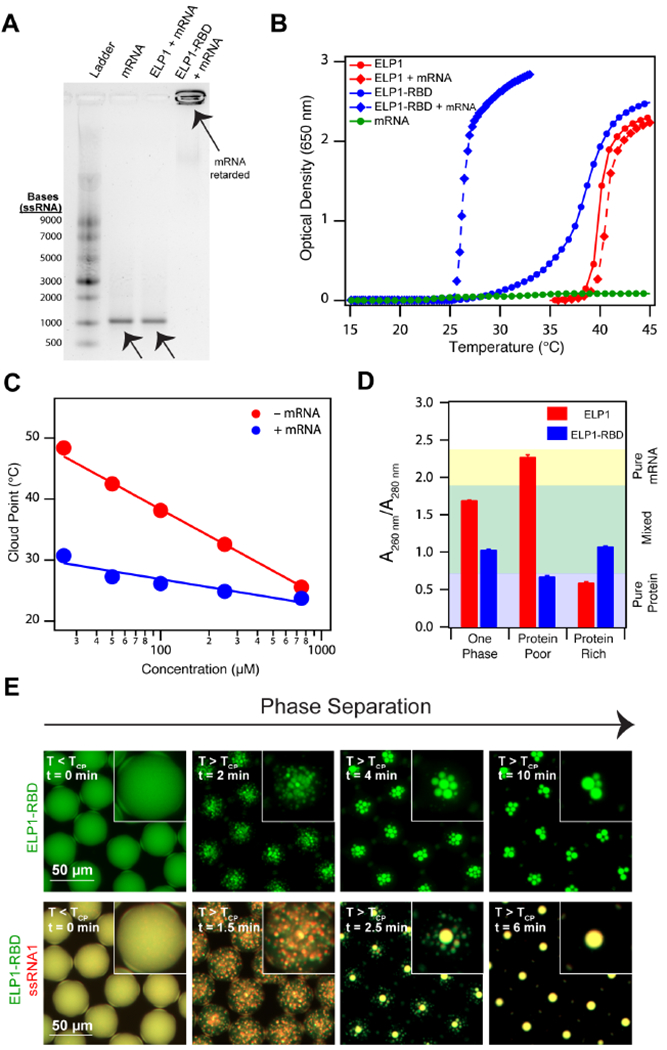
(A) 1% agarose gel stained with SYBR® Green II illustrating ELP1-RBD binds mRNA, whereas a control ELP lacking the RBD does not. ELP1 and ELP1-RBD concentration is 500 μM. eGFP mRNA concentration is 100 μg ml−1. (B) Optical density as a function of temperature of ELP1 with (red diamonds) and without (red circles) mRNA, ELP1-RBD with (blue diamonds) and without (blue circles) mRNA, and mRNA (green circles) in 1x PBS. Protein concentrations are 100 μM and eGFP concentration is 100 μg ml−1. (C) TCP as a function of concentration for ELP1-RBD (red points) and ELP1-RBD in the presence of mRNA (blue points) in 1x PBS. eGFP mRNA concentration is 100 μg ml−1. The solid lines represent the best logarithmic fit. (D) Nucleic acid quantitation of mixtures of ELP1 + mRNA (red) and ELP1-RBD + mRNA (blue) as a mixed, one phase solution before phase separation (left), a protein-poor phase after phase separation (middle), and a protein-rich phase after phase separation (right) in bulk. Starting ELP1 and ELP1-RBD concentrations are 500 μM and eGFP mRNA concentration is 100 μg ml−1. Error bars represent the SEM (n=3). (E) Fluorescence microscopy images of Alexa Fluor® 488-labeled ELP1-RBD (green)and Alexa Fluor® 594-labeled ssRNA1 (red) in microdroplets demonstrate that ELP1-RBD can co-phase separate with ssRNA upon heating above the TCP. ELP1-RBD concentration is 500 μM and ssRNA1 concentration is 2.5 μM. Related to Supplementary Tables 1 and 2, Supplementary Figures 1 and 2, and Supplementary Movies 1–3.
